Tyrosine phosphorylation of Sprouty proteins regulates their ability to inhibit growth factor signaling: a dual feedback loop
- PMID: 15004239
- PMCID: PMC404014
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-07-0503
Tyrosine phosphorylation of Sprouty proteins regulates their ability to inhibit growth factor signaling: a dual feedback loop
Retraction in
-
Retraction.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 Jul 1;33(8):re3. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E03-07-0503-corr. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35736612 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
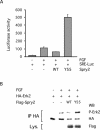
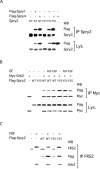
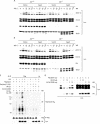
Sprouty proteins are recently identified receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitors potentially involved in many developmental processes. Here, we report that Sprouty proteins become tyrosine phosphorylated after growth factor treatment. We identified Tyr55 as a key residue for Sprouty2 phosphorylation and showed that phosphorylation was required for Sprouty2 to inhibit RTK signaling, because a mutant Sprouty2 lacking Tyr55 augmented signaling. We found that tyrosine phosphorylation of Sprouty2 affected neither its subcellular localization nor its interaction with Grb2, FRS2/SNT, or other Sprouty proteins. In contrast, Sprouty2 tyrosine phosphorylation was necessary for its binding to the Src homology 2-like domain of c-Cbl after fibroblast growth factor (FGF) stimulation. To determine whether c-Cbl was required for Sprouty2-dependent cellular events, Sprouty2 was introduced into c-Cbl-wild-type and -null fibroblasts. Sprouty2 efficiently inhibited FGF-induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in c-Cbl-null fibroblasts, thus indicating that the FGF-dependent binding of c-Cbl to Sprouty2 was dispensable for its inhibitory activity. However, c-Cbl mediates polyubiquitylation/proteasomal degradation of Sprouty2 in response to FGF. Last, using Src-family pharmacological inhibitors and dominant-negative Src, we showed that a Src-like kinase was required for tyrosine phosphorylation of Sprouty2 by growth factors. Thus, these data highlight a novel negative and positive regulatory loop that allows for the controlled, homeostatic inhibition of RTK signaling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cbl functions downstream of Src kinases in Fc gamma RI signaling in primary human macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Apr;65(4):523-34. doi: 10.1002/jlb.65.4.523. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10204582
-
Sprouty fine-tunes EGF signaling through interlinked positive and negative feedback loops.Curr Biol. 2003 Feb 18;13(4):297-307. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00053-8. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12593795
-
Sprouty2 acts at the Cbl/CIN85 interface to inhibit epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation.EMBO Rep. 2005 Jul;6(7):635-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400453. EMBO Rep. 2005. PMID: 15962011 Free PMC article.
-
CSF-1 signal transduction.J Leukoc Biol. 1997 Aug;62(2):145-55. doi: 10.1002/jlb.62.2.145. J Leukoc Biol. 1997. PMID: 9261328 Review.
-
Regulation of growth factor signaling by FRS2 family docking/scaffold adaptor proteins.Cancer Sci. 2008 Jul;99(7):1319-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00840.x. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18452557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal Delivery of AntagomiRs Targeting Viral and Cellular MicroRNAs Synergistically Inhibits Cancer Angiogenesis.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Aug 19;22:153-165. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.08.017. Online ahead of print. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32927364 Free PMC article.
-
Sprouty-2 overexpression in C2C12 cells confers myogenic differentiation properties in the presence of FGF2.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Sep;16(9):4454-61. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-05-0419. Epub 2005 Jul 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16000370 Free PMC article.
-
Sprouty2 downregulates angiogenesis during mouse skin wound healing.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Feb;300(2):H459-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00244.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 12. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21076020 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor adaptation and resistance to RAF inhibitors.Nat Med. 2013 Nov;19(11):1401-9. doi: 10.1038/nm.3392. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 24202393 Review.
-
Regulation of sprouty stability by Mnk1-dependent phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(5):1898-907. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.5.1898-1907.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16479008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blom, N., Gammeltoft, S., and Brunak, S. (1999). Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J. Mol. Biol. 294, 1351–1362. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M.T., and Cooper, J.A. (1996). Regulation, substrates and functions of src. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1287, 121–149. - PubMed
-
- Campbell, S.L., Khosravi-Far, R., Rossman, K.L., Clark, G.J., and Der, C.J. (1998). Increasing complexity of Ras signaling. Oncogene 17, 1395–1413. - PubMed
-
- Casci, T., Vinos, J., and Freeman, M. (1999). Sprouty, an intracellular inhibitor of Ras signaling. Cell 96, 655–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

