Lessons from the genome sequence of Neurospora crassa: tracing the path from genomic blueprint to multicellular organism
- PMID: 15007097
- PMCID: PMC362109
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.68.1.1-108.2004
Lessons from the genome sequence of Neurospora crassa: tracing the path from genomic blueprint to multicellular organism
Abstract
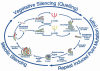
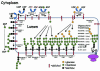
We present an analysis of over 1,100 of the approximately 10,000 predicted proteins encoded by the genome sequence of the filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa. Seven major areas of Neurospora genomics and biology are covered. First, the basic features of the genome, including the automated assembly, gene calls, and global gene analyses are summarized. The second section covers components of the centromere and kinetochore complexes, chromatin assembly and modification, and transcription and translation initiation factors. The third area discusses genome defense mechanisms, including repeat induced point mutation, quelling and meiotic silencing, and DNA repair and recombination. In the fourth section, topics relevant to metabolism and transport include extracellular digestion; membrane transporters; aspects of carbon, sulfur, nitrogen, and lipid metabolism; the mitochondrion and energy metabolism; the proteasome; and protein glycosylation, secretion, and endocytosis. Environmental sensing is the focus of the fifth section with a treatment of two-component systems; GTP-binding proteins; mitogen-activated protein, p21-activated, and germinal center kinases; calcium signaling; protein phosphatases; photobiology; circadian rhythms; and heat shock and stress responses. The sixth area of analysis is growth and development; it encompasses cell wall synthesis, proteins important for hyphal polarity, cytoskeletal components, the cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase machinery, macroconidiation, meiosis, and the sexual cycle. The seventh section covers topics relevant to animal and plant pathogenesis and human disease. The results demonstrate that a large proportion of Neurospora genes do not have homologues in the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. The group of unshared genes includes potential new targets for antifungals as well as loci implicated in human and plant physiology and disease.
Figures









References
-
- Aaronson, L. R., and C. E. Martin. 1983. Temperature-induced modifications of glycosphingolipids in plasma membranes of Neurospora crassa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 735:252-258. - PubMed
-
- Adams, M. D., S. E. Celniker, R. A. Holt, C. A. Evans, J. D. Gocayne, P. G. Amanatides, S. E. Scherer, P. W. Li, R. A. Hoskins, R. F. Galle, R. A. George, S. E. Lewis, S. Richards, M. Ashburner, S. N. Henderson, G. G. Sutton, J. R. Wortman, M. D. Yandell, Q. Zhang, L. X. Chen, R. C. Brandon, Y. H. Rogers, R. G. Blazej, M. Champe, B. D. Pfeiffer, K. H. Wan, C. Doyle, E. G. Baxter, G. Helt, C. R. Nelson, G. L. Gabor, J. F. Abril, A. Agbayani, H. J. An, C. Andrews-Pfannkoch, D. Baldwin, R. M. Ballew, A. Basu, J. Baxendale, L. Bayraktaroglu, E. M. Beasley, K. Y. Beeson, P. V. Benos, B. P. Berman, D. Bhandari, S. Bolshakov, D. Borkova, M. R. Botchan, J. Bouck, P. Brokstein, P. Brottier, K. C. Burtis, D. A. Busam, H. Butler, E. Cadieu, A. Center, I. Chandra, J. M. Cherry, S. Cawley, C. Dahlke, L. B. Davenport, P. Davies, B. de Pablos, A. Delcher, Z. Deng, A. D. Mays, I. Dew, S. M. Dietz, K. Dodson, L. E. Doup, M. Downes, S. Dugan-Rocha, B. C. Dunkov, P. Dunn, K. J. Durbin, C. C. Evangelista, C. Ferraz, S. Ferriera, W. Fleischmann, C. Fosler, A. E. Gabrielian, N. S. Garg, W. M. Gelbart, K. Glasser, A. Glodek, F. Gong, J. H. Gorrell, Z. Gu, P. Guan, M. Harris, N. L. Harris, D. Harvey, T. J. Heiman, J. R. Hernandez, J. Houck, D. Hostin, K. A. Houston, T. J. Howland, M. H. Wei, C. Ibegwam, et al. 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287:2185-2195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM034985/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM48626/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM58529/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM058770/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM034985/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH044651/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM068087/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S06 GM053933/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM58770/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM035690/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S06 GM53933/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM032677/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062377/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM34985/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM035690/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM058529/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM048626/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM35690/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH44651/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS039546/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS39546/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

