Fhit is a physiological target of the protein kinase Src
- PMID: 15007172
- PMCID: PMC374320
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0400481101
Fhit is a physiological target of the protein kinase Src
Abstract
The FHIT gene is a tumor suppressor that is frequently inactivated by genomic alterations at chromosomal region 3p14.2. In the last few years, a considerable amount of data describing inactivation of FHIT in a variety of human malignancies and demonstrating the tumor suppressor potential of Fhit have been reported. Despite the demonstration that FHIT functions as a tumor suppressor, the pathway through which Fhit induces apoptosis and inhibits growth of cancer cells is not known. Our data demonstrate that Fhit is a target of tyrosine phosphorylation by the Src protein kinase. We show that Src phosphorylates Y114 of Fhit in vitro and in vivo, providing insight into a biochemical pathway involved in Fhit signaling.
Figures

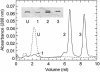
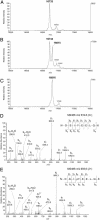

Similar articles
-
FHIT-proteasome degradation caused by mitogenic stimulation of the EGF receptor family in cancer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Dec 12;103(50):18981-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605821103. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17142325 Free PMC article.
-
Fhit modulation of the Akt-survivin pathway in lung cancer cells: Fhit-tyrosine 114 (Y114) is essential.Oncogene. 2006 May 11;25(20):2860-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209323. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16407838
-
Activation state-dependent interaction between Gαq subunits and the Fhit tumor suppressor.Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Aug 15;11:59. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-59. Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23947369 Free PMC article.
-
FHIT as tumor suppressor: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Cancer Biol Ther. 2002 May-Jun;1(3):232-6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.73. Cancer Biol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12432269 Review.
-
[FHIT--tumor suppressor protein involved in induction of apoptosis and cell cycle regulation].Postepy Biochem. 2009;55(1):66-75. Postepy Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19514467 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Chemical Proteomics of the Tumor Suppressor Fhit Covalently Bound to the Cofactor Ap3A Elucidates Its Inhibitory Action on Translation.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 May 18;144(19):8613-8623. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c00815. Epub 2022 May 6. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 35522782 Free PMC article.
-
FHIT-proteasome degradation caused by mitogenic stimulation of the EGF receptor family in cancer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Dec 12;103(50):18981-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605821103. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17142325 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive characterization of the genomic alterations in human gastric cancer.Int J Cancer. 2015 Jul 1;137(1):86-95. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29352. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25422082 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of FHIT, PCNA and EGFR in benign and malignant breast lesions.Br J Cancer. 2007 Jan 15;96(1):110-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603512. Epub 2006 Dec 12. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17164758 Free PMC article.
-
Fhit modulation of the Akt-survivin pathway in lung cancer cells: Fhit-tyrosine 114 (Y114) is essential.Oncogene. 2006 May 11;25(20):2860-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209323. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16407838
References
-
- Ohta, M., Inoue, H., Cotticelli, M. G., Kastury, K., Baffa, R., Palazzo, J., Siprashvili, Z., Mori, M., McCue, P., Druck, T. et al. (1996) Cell 84, 587-597. - PubMed
-
- Sozzi, G., Tornielli, S., Tagliabue, E., Sard, L., Pezzella, F., Pastorino, U., Minoletti, F., Pilotti, S., Ratcliffe, C., Veronese, M. L., et al. (1997) Cancer Res. 57, 5207-5712. - PubMed
-
- Baffa, R., Veronese, M. L., Santoro, R., Mandes, B., Palazzo, J. P., Rugge, M., Santoro, E., Croce, C. M. & Huebner, K. (1998) Cancer Res. 58, 4708-4714. - PubMed
-
- Campiglio, M., Pekarsky, Y., Menard, S., Tagliabue, E., Pilotti, S. & Croce, C. M. (1999) Cancer Res. 59, 3866-3869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

