The severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus replicative protein nsp9 is a single-stranded RNA-binding subunit unique in the RNA virus world
- PMID: 15007178
- PMCID: PMC374323
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307877101
The severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus replicative protein nsp9 is a single-stranded RNA-binding subunit unique in the RNA virus world
Abstract
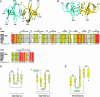
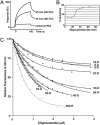
The recently identified etiological agent of the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) belongs to Coronaviridae (CoV), a family of viruses replicating by a poorly understood mechanism. Here, we report the crystal structure at 2.7-A resolution of nsp9, a hitherto uncharacterized subunit of the SARS-CoV replicative polyproteins. We show that SARS-CoV nsp9 is a single-stranded RNA-binding protein displaying a previously unreported, oligosaccharide/oligonucleotide fold-like fold. The presence of this type of protein has not been detected in the replicative complexes of RNA viruses, and its presence may reflect the unique and complex CoV viral replication/transcription machinery.
Figures

References
-
- Drosten, C., Gunther, S., Preiser, W., van der Werf, S., Brodt, H. R., Becker, S., Rabenau, H., Panning, M., Kolesnikova, L., Fouchier, R. A., et al. (2003) N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1967-1976. - PubMed
-
- Ksiazek, T. G., Erdman, D., Goldsmith, C. S., Zaki, S. R., Peret, T., Emery, S., Tong, S., Urbani, C., Comer, J. A., Lim, W., et al. (2003) N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1953-1966. - PubMed
-
- Marra, M. A., Jones, S. J., Astell, C. R., Holt, R. A., Brooks-Wilson, A., Butterfield, Y. S., Khattra, J., Asano, J. K., Barber, S. A., Chan, S. Y., et al. (2003) Science 300, 1399-1404. - PubMed
-
- Rota, P. A., Oberste, M. S., Monroe, S. S., Nix, W. A., Campagnoli, R., Icenogle, J. P., Penaranda, S., Bankamp, B., Maher, K., Chen, M. H., et al. (2003) Science 300, 1394-1399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

