Vestibular defects in head-tilt mice result from mutations in Nox3, encoding an NADPH oxidase
- PMID: 15014044
- PMCID: PMC374230
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1172504
Vestibular defects in head-tilt mice result from mutations in Nox3, encoding an NADPH oxidase
Abstract
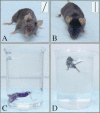
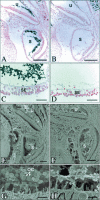
The vestibular system of the inner ear is responsible for the perception of motion and gravity. Key elements of this organ are otoconia, tiny biomineral particles in the utricle and the saccule. In response to gravity or linear acceleration, otoconia deflect the stereocilia of the hair cells, thus transducing kinetic movements into sensorineural action potentials. Here, we present an allelic series of mutations at the otoconia-deficient head tilt (het) locus, affecting the gene for NADPH oxidase 3 (Nox3). This series of mutations identifies for the first time a protein with a clear enzymatic function as indispensable for otoconia morphogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Otoconin-90 deletion leads to imbalance but normal hearing: a comparison with other otoconia mutants.Neuroscience. 2008 Apr 22;153(1):289-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.055. Epub 2008 Feb 10. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18355969 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired perception of gravity leads to altered head direction signals: what can we learn from vestibular-deficient mice?J Neurophysiol. 2009 Jul;102(1):12-4. doi: 10.1152/jn.00351.2009. Epub 2009 May 20. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19458147
-
Physical mapping of the mouse tilted locus identifies an association between human deafness loci DFNA6/14 and vestibular system development.Genomics. 2001 Oct;77(3):189-99. doi: 10.1006/geno.2001.6632. Genomics. 2001. PMID: 11597144
-
Vestibulo-ocular physiology underlying vestibular hypofunction.Phys Ther. 2004 Apr;84(4):373-85. Phys Ther. 2004. PMID: 15049730 Review.
-
Gravity or translation: central processing of vestibular signals to detect motion or tilt.J Vestib Res. 2003;13(4-6):245-53. J Vestib Res. 2003. PMID: 15096668 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of NADPH Oxidases in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Ischemic Stroke.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 30;11(10):1966. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101966. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency causes pulmonary emphysema.J Clin Invest. 2006 Nov;116(11):3050-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI28139. Epub 2006 Oct 19. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 17053835 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, functional, and structural analysis of proteins critical for otoconia development.Dev Dyn. 2010 Oct;239(10):2659-73. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22405. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 20803598 Free PMC article.
-
Spring brings breezes, wheezes, and pollen oxidases.J Clin Invest. 2005 Aug;115(8):2067-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI26023. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16075049 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidases in bone homeostasis and osteoporosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jan;72(1):25-38. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1712-2. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25167924 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banfi B., Molnar, G., Maturana, A., Steger, K., Hegedus, B., Demaurex, N., and Krause, K.H. 2001. A Ca(2+)-activated NADPH oxidase in testis, spleen, and lymph nodes. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 37594–37601. - PubMed
-
- Cheng G., Cao, Z., Xu, X., van Meir, E.G., and Lambeth, J.D. 2001. Homologs of gp91phox: Cloning and tissue expression of Nox3, Nox4, and Nox5. Gene 269: 131–140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
