Motor outputs from the primate reticular formation to shoulder muscles as revealed by stimulus-triggered averaging
- PMID: 15014106
- PMCID: PMC2740726
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00083.2003
Motor outputs from the primate reticular formation to shoulder muscles as revealed by stimulus-triggered averaging
Abstract
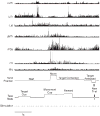
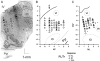
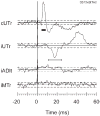
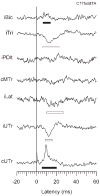
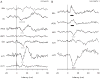
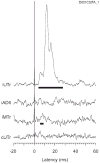
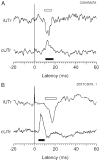
The motor output of the medial pontomedullary reticular formation (mPMRF) was investigated using stimulus-triggered averaging (StimulusTA) of EMG responses from proximal arm and shoulder muscles in awake, behaving monkeys (M. fascicularis). Muscles studied on the side ipsilateral (i) to stimulation were biceps (iBic), triceps (iTri), anterior deltoid (iADlt), posterior deltoid (iPDlt), and latissimus dorsi (iLat). The upper and middle trapezius were studied on the ipsilateral and contralateral (c) side (iUTr, cUTr, iMTr, cMTr). Of 133 sites tested, 97 (73%) produced a poststimulus effect (PStE) in one or more muscles; on average, 38% of the sampled muscles responded per effective site. For responses that were observed in the arm and shoulder, poststimulus facilitation (PStF) was prevalent for the flexors, iBic (8 responses, 100% PStF) and iADlt (13 responses, 77% PStF), and poststimulus suppression (PStS) was prevalent for the extensors, iTri (22 responses, 96% PStS) and iLat (16 responses, 81% PStS). For trapezius muscles, PStS of upper trapezius (iUTr, 49 responses, 73% PStS) and PStF of middle trapezius (iMTr, 22 responses, 64% PStF) were prevalent ipsilaterally, and PStS of middle trapezius (cMTr, 6 responses, 67% PStS) and PStF of upper trapezius (cUTr, 46 responses, 83% PStS) were prevalent contralaterally. Onset latencies were significantly earlier for PStF (7.0 +/- 2.2 ms) than for PStS (8.6 +/- 2.0 ms). At several sites, extremely strong PStF was evoked in iUTr, even though PStS was most common for this muscle. The anatomical antagonists iBic/iTri were affected reciprocally when both responded. The bilateral muscle pair iUTr/cUTr demonstrated various combinations of effects, but cUTr PStF with iUTr PStS was prevalent. Overall, the results are consistent with data from the cat and show that outputs from the mPMRF can facilitate or suppress activity in muscles involved in reaching; responses that would contribute to flexion of the ipsilateral arm were prevalent.
Figures



References
-
- Alstermark B, Kummel H, Tantisira B. Monosynaptic raphespinal and reticulospinal projection to forelimb motoneurones in cats. Neurosci Lett. 1987;74:286–290. - PubMed
-
- Belhaj-Saif A, Karrer JH, Cheney PD. Distribution and characteristics of poststimulus effects in proximal and distal forelimb muscles from red nucleus in the monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:1777–1789. - PubMed
-
- Betts B, Smith JL, Edgerton VR, Collatos TC. Telemetered EMG of fast and slow muscles in cats. Brain Res. 1976;117:529–533. - PubMed
-
- Bolton PS, Goto T, Schor RH, Wilson VJ, Yamagata Y, Yates BJ. Response of pontomedullary reticulospinal neurons to vestibular stimuli in vertical planes. Role in vertical vestibulospinal reflexes of the decerebrate cat. J Neurophysiol. 1992;67:639–647. - PubMed
-
- Bowden D, Dubach M, MacArthur E, Song E. BrainInfo (2000) Neuroscience Division, Regional Primate Research Center, University of Washington; 2003. Electronic Citation.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

