Synaptic vesicles: test for a role in presynaptic calcium regulation
- PMID: 15014125
- PMCID: PMC6729477
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5372-03.2004
Synaptic vesicles: test for a role in presynaptic calcium regulation
Abstract
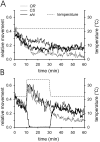
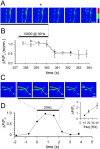
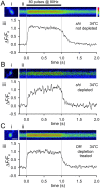
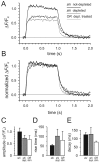
Membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum play an important role in neuronal Ca(2+) homeostasis. Synaptic vesicles (SVs), the organelles responsible for exocytosis of neurotransmitters, occupy more of the volume of presynaptic nerve terminals than any other organelle and, under some conditions, can accumulate Ca(2+). They are also closely associated with voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels (VGCCs) that trigger transmitter release by admitting Ca(2+) into the nerve terminal in response to action potentials (APs). We tested the hypothesis that SVs can modulate Ca(2+) signals in the presynaptic terminal. This has been a difficult question to address because neither pharmacological nor genetic approaches to block Ca(2+) permeation of the SV membrane have been available. To investigate the possible role of SVs in Ca(2+) regulation, we used imaging techniques to compare Ca(2+) dynamics in motor nerve terminals before and after depletion of SVs. We used the temperature-sensitive Drosophila dynamin mutant shibire, in which SVs can be eliminated by stimulation. There was no difference in the amplitude or time course of Ca(2+) responses during high-frequency trains of APs, or single APs, in individual presynaptic boutons before and after depletion of SVs. SVs have a limited role, if any, in the rapid sequestration of Ca(2+) within the neuronal cytosol or the synaptic microdomain. We also conclude that SVs are not important for regulation of synaptic VGCCs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Drosophila cacts2 mutation reduces presynaptic Ca2+ entry and defines an important element in Cav2.1 channel inactivation.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Jun;23(12):3230-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04873.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16820014
-
Separation of presynaptic Cav2 and Cav1 channel function in synaptic vesicle exo- and endocytosis by the membrane anchored Ca2+ pump PMCA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jul 13;118(28):e2106621118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2106621118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34244444 Free PMC article.
-
Exocytosis and endocytosis of synaptic vesicles and functional roles of vesicle pools: lessons from the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.Neuroscientist. 2005 Apr;11(2):138-47. doi: 10.1177/1073858404271679. Neuroscientist. 2005. PMID: 15746382 Review.
-
Presynaptic loss of dynamin-related protein 1 impairs synaptic vesicle release and recycling at the mouse calyx of Held.J Physiol. 2018 Dec;596(24):6263-6287. doi: 10.1113/JP276424. Epub 2018 Nov 10. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30285293 Free PMC article.
-
Two synaptic vesicle pools, vesicle recruitment and replenishment of pools at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.J Neurocytol. 2003 Jun-Sep;32(5-8):551-65. doi: 10.1023/B:NEUR.0000020610.13554.3c. J Neurocytol. 2003. PMID: 15034253 Review.
Cited by
-
Serotonergic Modulation Enables Pathway-Specific Plasticity in a Developing Sensory Circuit in Drosophila.Neuron. 2017 Aug 2;95(3):623-638.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.06.034. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 28712652 Free PMC article.
-
cGMP-Dependent Protein Kinase Inhibition Extends the Upper Temperature Limit of Stimulus-Evoked Calcium Responses in Motoneuronal Boutons of Drosophila melanogaster Larvae.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0164114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164114. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711243 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol and F-actin are required for clustering of recycling synaptic vesicle proteins in the presynaptic plasma membrane.J Physiol. 2014 Feb 15;592(4):621-33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.265447. Epub 2013 Dec 2. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24297851 Free PMC article.
-
A synaptic vesicle-associated Ca2+ channel promotes endocytosis and couples exocytosis to endocytosis.Cell. 2009 Sep 4;138(5):947-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.033. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19737521 Free PMC article.
-
Neto-α Controls Synapse Organization and Homeostasis at the Drosophila Neuromuscular Junction.Cell Rep. 2020 Jul 7;32(1):107866. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107866. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32640231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atwood HL, Govind CK, Wu C-F (1993) Differential ultrastructure of synaptic terminals on ventral longitudinal abdominal muscles in Drosophila larvae. J Neurobiol 24: 1008-1024. - PubMed
-
- Barclay JW, Atwood HL, Robertson RM (2002) Impairment of central pattern generation in Drosophila cysteine string protein mutants. J Comp Physiol 88: 71-78. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL (2003) Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 517-529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
