Role of calcium in neurotensin-evoked enhancement in firing in mesencephalic dopamine neurons
- PMID: 15014132
- PMCID: PMC6729478
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5376-03.2004
Role of calcium in neurotensin-evoked enhancement in firing in mesencephalic dopamine neurons
Abstract
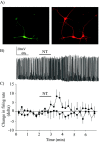
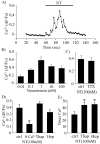
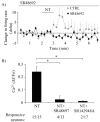
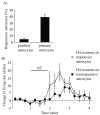
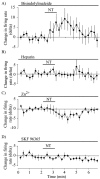
Neurotensin (NT) increases neurotransmission within the mesolimbic dopamine system by enhancing the firing rate of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons and by acting at the nerve terminal level. The signal transduction pathways involved in these effects have not been characterized, but NT receptors are coupled to the phospholipase C pathway and Ca(2+) mobilization. However, an enhancement of intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) evoked by NT in DAergic neurons has yet to be demonstrated. Furthermore, the hypothesis that the excitatory effects of NT in DAergic neurons are Ca(2+) dependent is currently untested. In whole-cell recording experiments, DAergic neurons in culture were identified by their selective ability to express a cell-specific green fluorescent protein reporter construct. These experiments confirmed that NT increases firing rate in cultured DAergic neurons. This effect was Ca(2+) dependent because it was blocked by intracellular dialysis with BAPTA. Using Ca(2+) imaging, we showed that NT caused a rapid increase in [Ca(2+)](i) in DAergic neurons. Most of the Ca(2+) originated from the extracellular medium. NT-induced excitation and Ca(2+) influx were blocked by SR48692, an antagonist of the type 1 NT receptor. Blocking IP(3) receptors using heparin prevented the excitatory effect of NT. Moreover, Zn(2+) and SKF96365 both blocked the excitatory effect of NT, suggesting that nonselective cationic conductances are involved. Finally, although NT can also induce a rise in [Ca(2+)](i) in astrocytes, we find that NT-evoked excitation of DAergic neurons can occur independently of astrocyte activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurotensin excitation of serotonergic neurons in the rat nucleus raphe magnus: ionic and molecular mechanisms.Neuropharmacology. 2001 Jun;40(8):1073-83. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(01)00030-2. Neuropharmacology. 2001. PMID: 11406199
-
Bidirectional regulation of dopamine D2 and neurotensin NTS1 receptors in dopamine neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Nov;24(10):2789-800. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05151.x. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17116165
-
Neurotensin modulates the amplitude and frequency of voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in frog pituitary melanotrophs: implication of the inositol triphosphate/protein kinase C pathway.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Nov;16(10):1907-16. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02296.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12453054
-
Neurotensin inhibits background K+ channels and facilitates glutamatergic transmission in rat spinal cord dorsal horn.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Oct;34(8):1230-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07846.x. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21936876
-
Neurotensin Induces Presynaptic Depression of D2 Dopamine Autoreceptor-Mediated Neurotransmission in Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 5;35(31):11144-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3816-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26245975 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between neurotensin receptor 1 gene polymorphisms and alcohol dependence in a male Han Chinese population.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Oct;51(2):408-15. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-0041-5. Epub 2013 Jun 8. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23743782
-
Association of Neurotensin Receptor 1 Gene Polymorphisms With Defense Mechanisms in Healthy Chinese.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Nov 17;12:762276. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.762276. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34867546 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral hypothalamic neurotensin neurons promote arousal and hyperthermia.PLoS Biol. 2019 Mar 20;17(3):e3000172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000172. eCollection 2019 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 30893297 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic action of neurotensin on dopamine release through inhibition of D(2) receptor function.BMC Neurosci. 2009 Aug 14;10:96. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-96. BMC Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19682375 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotensin triggers dopamine D2 receptor desensitization through a protein kinase C and beta-arrestin1-dependent mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 18;286(11):9174-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.166454. Epub 2011 Jan 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21233215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Billah MM, Lapetina EG, Cuatrecasas P (1980) Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C activities of platelets. Differential substrate specificity, Ca2+ requirement, pH dependence, and cellular localization. J Biol Chem 255: 10227-10231. - PubMed
-
- Borges S, Gleason E, Frerking M, Wilson M (1996) Neurotensin induces calcium oscillations in cultured amacrine cells. Vis Neurosci 13: 311-318. - PubMed
-
- Boulay G, Zhu X, Peyton M, Jiang M, Hurst R, Stefani E, Birnbaumer L (1997) Cloning and expression of a novel mammalian homolog of Drosophila transient receptor potential (Trp) involved in calcium entry secondary to activation of receptors coupled by the Gq class of G protein. J Biol Chem 272: 29672-29680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
