Structure of the translocator domain of a bacterial autotransporter
- PMID: 15014442
- PMCID: PMC381419
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600148
Structure of the translocator domain of a bacterial autotransporter
Abstract
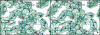
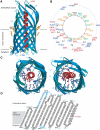
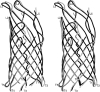
Autotransporters are virulence-related proteins of Gram-negative bacteria that are secreted via an outer-membrane-based C-terminal extension, the translocator domain. This domain supposedly is sufficient for the transport of the N-terminal passenger domain across the outer membrane. We present here the crystal structure of the in vitro-folded translocator domain of the autotransporter NalP from Neisseria meningitidis, which reveals a 12-stranded beta-barrel with a hydrophilic pore of 10 x 12.5 A that is filled by an N-terminal alpha-helix. The domain has pore activity in vivo and in vitro. Our data are consistent with the model of passenger-domain transport through the hydrophilic channel within the beta-barrel, and inconsistent with a model for transport through a central channel formed by an oligomer of translocator domains. However, the dimensions of the pore imply translocation of the secreted domain in an unfolded form. An alternative model, possibly covering the transport of folded domains, is that passenger-domain transport involves the Omp85 complex, the machinery required for membrane insertion of outer-membrane proteins, on which autotransporters are dependent.
Figures

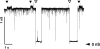
References
-
- Bosch D, Leunissen J, Verbakel J, de Jong M, van Erp H, Tommassen J (1986) Periplasmic accumulation of truncated forms of outer-membrane PhoE protein of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol 189: 449–455 - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D 54: 905–921 - PubMed
-
- CCP4 (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D 50: 760–763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
