Treatment of colorectal and hepatocellular carcinomas by adenoviral mediated gene transfer of endostatin and angiostatin-like molecule in mice
- PMID: 15016752
- PMCID: PMC1774006
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2003.019307
Treatment of colorectal and hepatocellular carcinomas by adenoviral mediated gene transfer of endostatin and angiostatin-like molecule in mice
Abstract
Aim and method: In this study, we explored the responsiveness of different tumour entities (colorectal carcinoma (CRC), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and the murine Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC)) to angiostatic antitumour treatment with two recombinant adenoviral vectors encoding angiostatin-like molecule (AdK1-3) and endostatin (Adendo).
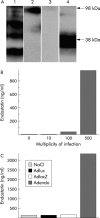
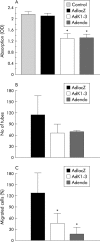
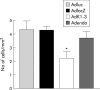
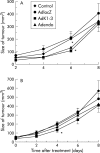
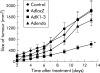
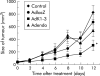
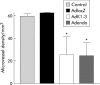
Results: AdK1-3 and Adendo exerted inhibitory biological functions on endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation in vitro. AdK1-3 inhibited significantly endothelial cell infiltration in vascular endothelial growth factor embedded Matrigel plugs in mice whereas Adendo showed only minor effects. Both AdK1-3 and Adendo induced similar antitumour effects in the LLC tumour model in immune competent C57BL/6 mice but AdK1-3 had stronger inhibitory effects in athymic mice. Furthermore, AdK1-3 inhibited tumour growth in a murine CRC and human HCC model but was ineffective in a human CRC model. In contrast, Adendo did not reduce tumour progress in either of these tumour models although AdK1-3 and Adendo effectively reduced intratumoral microvessel density in LLC tumours.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that angiostatic gene therapy may form a feasible strategy for the treatment of established hepatocellular carcinomas and that in vivo antitumour efficacy of angiostatic proteins is tumour specific.
Figures
References
-
- Ellis LM, Liu W, Ahmad SA, et al. Overview of angiogenesis: Biologic implications for antiangiogenic therapy. Semin Oncol 2001;28 (suppl 16):94–104. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y. Endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors and their therapeutic implications. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2001;33:357–69. - PubMed
-
- Gasparini G. The rationale and future potential of angiogenesis inhibitors in neoplasia. Drugs 1999;58:17–38. - PubMed
-
- Soff GA. Angiostatin and angiostatin-related proteins. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2000;19:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Griffioen AW, Molema G. Angiogenesis: potentials for pharmacologic intervention in the treatment of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic inflammation. Pharmacol Rev 2000;52:237–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
