p16(Ink4a) interferes with Abelson virus transformation by enhancing apoptosis
- PMID: 15016851
- PMCID: PMC371071
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3304-3311.2004
p16(Ink4a) interferes with Abelson virus transformation by enhancing apoptosis
Abstract
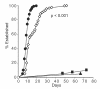
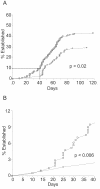
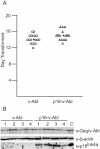
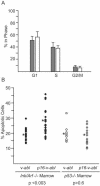
Pre-B-cell transformation by Abelson virus (Ab-MLV) is a multistep process in which primary transformants are stimulated to proliferate but subsequently undergo crisis, a period of erratic growth marked by high levels of apoptosis. Inactivation of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway is an important step in this process and can be accomplished by mutation of p53 or down-modulation of p19(Arf), a p53 regulatory protein. Consistent with these data, pre-B cells from either p53 or Ink4a/Arf null mice bypass crisis. However, the Ink4a/Arf locus encodes both p19(Arf) and a second tumor suppressor, p16(Ink4a), that blocks cell cycle progression by inhibiting Cdk4/6. To determine if p16(Ink4a) plays a role in Ab-MLV transformation, primary transformants derived from Arf(-/-) and p16(Ink4a(-/-)) mice were compared. A fraction of those derived from Arf(-/-) animals underwent crisis, and even though all p16(Ink4a(-/-)) primary transformants experienced crisis, these cells became established more readily than cells derived from +/+ mice. Analyses of Ink4a/Arf(-/-) cells infected with a virus that expresses both v-Abl and p16(Ink4a) revealed that p16(Ink4a) expression does not alter cell cycle profiles but does increase the level of apoptosis in primary transformants. These results indicate that both products of the Ink4a/Arf locus influence Ab-MLV transformation and reveal that in addition to its well-recognized effects on the cell cycle, p16(Ink4a) can suppress transformation by inducing apoptosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Changes in p19Arf localization accompany apoptotic crisis during pre-B-cell transformation by Abelson murine leukemia virus.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(17):8383-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00348-08. Epub 2008 Jun 25. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18579612 Free PMC article.
-
p19(Arf) induces p53-dependent apoptosis during abelson virus-mediated pre-B cell transformation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Oct 27;95(22):13194-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13194. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9789064 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of heterozygosity at the Ink4a/Arf locus facilitates Abelson virus transformation of pre-B cells.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(20):9479-87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.20.9479-9487.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11000217 Free PMC article.
-
The INK4a/ARF locus and melanoma.Oncogene. 2003 May 19;22(20):3092-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206461. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12789286 Review.
-
p53-Dependent and -independent functions of the Arf tumor suppressor.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:129-37. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2005.70.004. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005. PMID: 16869746 Review.
Cited by
-
Bcl-2 blocks 2-methoxyestradiol induced leukemia cell apoptosis by a p27(Kip1)-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest in conjunction with NF-kappaB activation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jul 1;78(1):33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.03.017. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19447221 Free PMC article.
-
Aging and cancer resistance in lymphoid progenitors are linked processes conferred by p16Ink4a and Arf.Genes Dev. 2008 Nov 15;22(22):3115-20. doi: 10.1101/gad.1715808. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 19056891 Free PMC article.
-
Forced expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 6 confers resistance of pro-B acute lymphocytic leukemia to Gleevec treatment.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul;31(13):2566-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01349-10. Epub 2011 May 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21536647 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in p19Arf localization accompany apoptotic crisis during pre-B-cell transformation by Abelson murine leukemia virus.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(17):8383-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00348-08. Epub 2008 Jun 25. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18579612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi, Y., S. S. Lakka, N. Chandrasekar, N. Yanamandra, C. S. Gondi, S. Mohanam, D. H. Dinh, W. C. Olivero, M. Gujrati, T. Tamiya, T. Ohmoto, G. Kouraklis, B. Aggarwal, and J. S. Rao. 2001. Down-regulation of integrin αvβ3 expression and integrin-mediated signaling in glioma cells by adenovirus-mediated transfer of anti-sense urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and sense p16 genes. J. Biol. Chem. 276:47171-47177. - PubMed
-
- Ausserlechner, M. J., P. Obexer, G. J. Wiegers, B. L. Hartmann, S. Geley, and R. Kofler. 2001. The cell cycle inhibitor p16(INK4A) sensitizes lymphoblastic leukemia cells to apoptosis by physiologic glucocorticoid levels. J. Biol. Chem. 276:10984-10989. - PubMed
-
- Bachoo, R. M., E. A. Maher, K. L. Ligon, N. E. Sharpless, S. S. Chan, M. J. You, Y. Tang, J. DeFrances, E. Stover, R. Weissleder, D. H. Rowitch, D. N. Louis, and R. A. DePinho. 2002. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell 1:269-277. - PubMed
-
- Calbo, J., M. Marotta, M. Cascallo, J. M. Roig, J. L. Gelpi, J. Fueyo, and A. Mazo. 2001. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of wt-p16 induces cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 8:740-750. - PubMed
-
- Calero Moreno, T. M., G. Gustagsson, S. Garwicz, D. Grander, G. K. Jonmundsson, B. M. Frost, A. Makipernaa, O. Rasool, E. R. Savolainen, K. Schmiegelow, S. Soderhall, K. Vettenranta, F. Wesenberg, S. Einhorn, and M. Heyman. 2002. Deletion of the Ink4-locus (the p16Ink4a, p14ARF and p15Ink4b genes) predicts relapse in children with ALL treated according to the Nordic protocols NOPHO-86 and NOPHO-92. Leukemia 16:2037-2045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

