The binding of histone deacetylases and the integrity of zinc finger-like motifs of the E7 protein are essential for the life cycle of human papillomavirus type 31
- PMID: 15016876
- PMCID: PMC371089
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3533-3541.2004
The binding of histone deacetylases and the integrity of zinc finger-like motifs of the E7 protein are essential for the life cycle of human papillomavirus type 31
Abstract
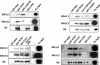
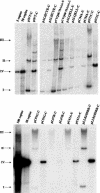
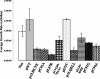
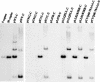
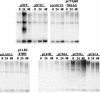
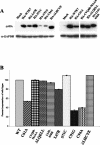
The E7 oncoprotein of high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPVs) binds to and alters the action of cell cycle regulatory proteins such as members of the retinoblastoma (Rb) family of proteins as well as the histone deacetylases (HDACs). To examine the significance of the binding of E7 to HDACs in the viral life cycle, a mutational analysis of the E7 open reading frame was performed in the context of the complete HPV type 31 (HPV-31) genome. Human foreskin keratinocytes were transfected with wild-type HPV-31 genomes or HPV-31 genomes containing mutations in HDAC binding sequences as well as in the C-terminal zinc finger-like domain, and stable cell lines were isolated. All mutant genomes, except those with E7 mutations in the HDAC binding site, were found to be stably maintained extrachromosomally at an early passage following transfection. Upon further passage in culture, genomes containing mutations to the Rb binding domain as well as the zinc finger-like region quickly lost the ability to maintain episomal genomes. Genomes containing mutations abolishing E7 binding to HDACs or to Rb or mutations to the zinc finger-like motifs failed to extend the life span of transfected keratinocytes and caused cells to arrest at the same time as the untransfected keratinocytes. When induced to differentiate by suspension in methylcellulose, cells maintaining genomes with mutations in the Rb binding domain or the zinc finger-like motifs were impaired in their abilities to activate late viral functions. This study demonstrates that the interaction of E7 with HDACs and the integrity of the zinc finger-like motifs are essential for extending the life span of keratinocytes and for stable maintenance of viral genomes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Roles of the E6 and E7 proteins in the life cycle of low-risk human papillomavirus type 11.J Virol. 2004 Mar;78(5):2620-6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.5.2620-2626.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14963169 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 maintains elevated levels of the cdc25A tyrosine phosphatase during deregulation of cell cycle arrest.J Virol. 2002 Jan;76(2):619-32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.2.619-632.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11752153 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of high-risk e6 in episomal maintenance of human papillomavirus genomes in primary human keratinocytes.J Virol. 2002 Nov;76(22):11359-64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11359-11364.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12388696 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular targets of the oncoproteins encoded by the cancer associated human papillomaviruses.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1991;22:239-48. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1991. PMID: 1668886 Review.
-
Biology of human papillomaviruses.Int J Exp Pathol. 2001 Feb;82(1):15-33. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2613.2001.00177.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11422538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Entry Inhibitors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1366:223-239. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-8702-0_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35412144
-
Human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein induces KDM6A and KDM6B histone demethylase expression and causes epigenetic reprogramming.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 1;108(5):2130-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009933108. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21245294 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia Virus as a Master of Host Shutoff Induction: Targeting Processes of the Central Dogma and Beyond.Pathogens. 2020 May 21;9(5):400. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050400. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32455727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human papillomaviruses: shared and distinct pathways for pathogenesis.Curr Opin Virol. 2015 Oct;14:87-92. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Sep 20. Curr Opin Virol. 2015. PMID: 26398222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of human papillomavirus type 31 gene expression during the differentiation-dependent life cycle through histone modifications and transcription factor binding.Virology. 2008 May 10;374(2):371-80. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.12.011. Epub 2008 Jan 31. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18237759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brehm, A., E. A. Miska, D. J. McCance, J. L. Reid, A. J. Bannister, and T. Kouzarides. 1998. Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nature 391:597-601. - PubMed
-
- Chellappan, S., V. B. Kraus, B. Kroger, K. Munger, P. M. Howley, W. C. Phelps, and J. R. Nevins. 1992. Adenovirus E1A, simian virus 40 tumor antigen, and human papillomavirus E7 protein share the capacity to disrupt the interaction between transcription factor E2F and the retinoblastoma gene product. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:4549-4553. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, J., P. Jackson, M. Kirschner, and A. Dutta. 1995. Separate domains of p21 involved in the inhibition of cdk kinase and PCNA. Nature 374:386-388. - PubMed
-
- Ciccolini, F., G. Di Pasquale, F. Carlotti, L. Crawford, and M. Tommasino. 1994. Functional studies of E7 proteins from different HPV types. Oncogene 9:2633-2638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

