Bacillus subtilis GlcK activity requires cysteines within a motif that discriminates microbial glucokinases into two lineages
- PMID: 15018644
- PMCID: PMC365027
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-4-6
Bacillus subtilis GlcK activity requires cysteines within a motif that discriminates microbial glucokinases into two lineages
Abstract
Background: Bacillus subtilis glucokinase (GlcK) (GenBank NP_390365) is an ATP-dependent kinase that phosphorylates glucose to glucose 6-phosphate. The GlcK protein has very low sequence identity (13.7%) to the Escherichia coli glucokinase (Glk) (GenBank P46880) and some other glucokinases (EC 2.7.1.2), yet glucose is merely its substrate. Our lab has previously isolated and characterized the glcK gene.
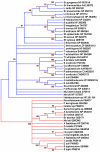
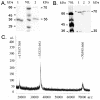
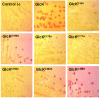
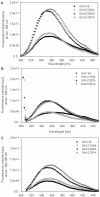
Results: Microbial glucokinases can be grouped into two different lineages. One of the lineages contains three conserved cysteine (C) residues in a CXCGX(2)GCXE motif. This motif is also present in the B. subtilis GlcK. The GlcK protein occurs in both monomer and homodimer. Each GlcK monomer has six cysteines. All cysteine residues have been mutated, one-by-one, into alanine (A). The in vivo GlcK enzymatic activity was assayed by functional complementation in E. coli UE26 (ptsG ptsM glk). Mutation of the three motif-specific residues led to an inactive enzyme. The other mutated forms retained, or in one case (GlcKC321A) even gained, activity. The fluorescence spectra of the GlcKC321A showed a red shift and enhanced fluorescence intensity compare to the wild type's.
Conclusions: Our results emphasize the necessity of cysteines within the CXCGX(2)GCXE motif for GlcK activity. On the other hand, the C321A mutation led to higher GlcKC321A enzymatic activity with respect to the wild type's, suggesting more adequate glucose phosphorylation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The glucose kinase of Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 1998 Jun;180(12):3222-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.12.3222-3226.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9620975 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and biochemical characterization of novel glucokinases from Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania spp.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2007 Dec;156(2):235-45. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2007.08.007. Epub 2007 Aug 26. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2007. PMID: 17904661
-
Molecular characterization of a glucokinase with broad hexose specificity from Bacillus sphaericus strain C3-41.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Jun;73(11):3581-6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02863-06. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17400775 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of a novel gene, gluP, is essential for normal Bacillus subtilis cell division and contributes to glucose export.BMC Microbiol. 2004 Mar 30;4:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-4-13. BMC Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15050034 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of Escherichia coli ATP-dependent glucokinase and its complex with glucose.J Bacteriol. 2004 Oct;186(20):6915-27. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.20.6915-6927.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15466045 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Low-Dose Amoxicillin on Staphylococcus aureus USA300 Biofilms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Apr 22;60(5):2639-51. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02070-15. Print 2016 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26856828 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing lysine acetylation of glucokinase.Protein Sci. 2024 Jan;33(1):e4845. doi: 10.1002/pro.4845. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 37996965 Free PMC article.
-
The basis for non-canonical ROK family function in the N-acetylmannosamine kinase from the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):3301-3315. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010526. Epub 2020 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31949045 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic engineering of carbohydrate metabolism systems in Corynebacterium glutamicum for improving the efficiency of L-lysine production from mixed sugar.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Feb 18;19(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-1294-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 32070345 Free PMC article.
-
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of a putative glucokinase/hexokinase from Thermus thermophilus.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011 Dec 1;67(Pt 12):1559-62. doi: 10.1107/S1744309111041145. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011. PMID: 22139166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson CM, McDonald RC, Steitz TA. Sequencing a protein by x-ray crystallography. I. Interpretation of yeast hexokinase B at 2.5 A resolution by model building. J Mol Biol. 1978;123:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Xu LZ, Zhang W, Weber IT, Harrison RW, Pilkis SJ. Site-directed mutagenesis studies on the determinants of sugar specificity and cooperative behavior of human beta-cell glucokinase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:27458–27465. - PubMed
-
- Mahalingam B, Cuesta-Munoz A, Davis EA, Matschinsky FM, Harrison RW, Weber IT. Structural model of human glucokinase in complex with glucose and ATP: implications for the mutants that cause hypo- and hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 1999;48:1698–1705. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

