Multiplex RT-nested PCR differentiation of gill-associated virus (Australia) from yellow head virus (Thailand) of Penaeus monodon
- PMID: 15019259
- PMCID: PMC7172704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2003.11.018
Multiplex RT-nested PCR differentiation of gill-associated virus (Australia) from yellow head virus (Thailand) of Penaeus monodon
Abstract
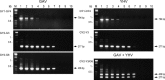
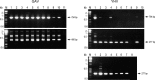
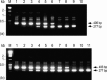
A multiplex RT-nested PCR has been developed to detect and differentiate the closely related prawn viruses, gill-associated virus (GAV) from Australia and yellow head virus (YHV) from Thailand. RT-PCR using primers to conserved sequences in the ORF1b gene amplified a 794 bp region of either GAV or YHV. Nested PCR using a conserved sense primer and either a GAV- or YHV-specific antisense primer to a divergent sequence differentially amplified a 277 bp region of the primary PCR amplicon. Multiplexing the YHV antisense primer with a GAV antisense primer to another divergent sequence allowed the viruses to be distinguished in a single nested PCR. Nested PCR enhanced detection sensitivity between 100- and 1000-fold and GAV or YHV RNA was detectable in approximately 10 fg lymphoid organ total RNA. The multiplex RT-nested PCR was also able to co-detect GAV and YHV RNA mixed over a wide range of concentrations to simulate potential dual-infection states. The robustness of the test was examined using RNA samples from Penaeus monodon prawns infected either chronically or acutely with GAV or YHV and collected at different locations in Eastern Australia and Thailand between 1994 and 1998. GAV- (406 bp) or YHV-specific (277 bp) amplicons were differentially generated in all cases, including five YHV RNA samples in which no primary RT-PCR amplicon was detected. Sequence analysis of GAV and YHV PCR amplicons identified minor variations in the regions targeted by the virus-specific antisense primers. However, none occurred at positions that critically affected the PCR.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vertical transmission of gill-associated virus (GAV) in the black tiger prawn Penaeus monodon.Dis Aquat Organ. 2002 Jul 8;50(2):95-104. doi: 10.3354/dao050095. Dis Aquat Organ. 2002. PMID: 12180710
-
Detection and differentiation of yellow head complex viruses using monoclonal antibodies.Dis Aquat Organ. 2003 Dec 29;57(3):193-200. doi: 10.3354/dao057193. Dis Aquat Organ. 2003. PMID: 14960031
-
Detection of Australian gill-associated virus (GAV) and lymphoid organ virus (LOV) of Penaeus monodon by RT-nested PCR.Dis Aquat Organ. 2000 Feb 9;39(3):159-67. doi: 10.3354/dao039159. Dis Aquat Organ. 2000. PMID: 10768283
-
Gill-associated virus of Penaeus monodon prawns. Molecular evidence for the first invertebrate nidovirus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;494:43-8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001. PMID: 11774504 Review. No abstract available.
-
Rapid and sensitive detection of shrimp yellow head virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick.J Virol Methods. 2013 Mar;188(1-2):51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2012.11.041. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Virol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23219929 Review.
Cited by
-
Coinfection with Yellow Head Virus Genotype 8 (YHV-8) and Oriental Wenrivirus 1 (OWV1) in Wild Penaeus chinensis from the Yellow Sea.Viruses. 2023 Jan 27;15(2):361. doi: 10.3390/v15020361. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851575 Free PMC article.
-
Viral disease emergence in shrimp aquaculture: origins, impact and the effectiveness of health management strategies.Rev Aquac. 2009 Jun;1(2):125-154. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-5131.2009.01007.x. Epub 2009 May 15. Rev Aquac. 2009. PMID: 32328167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid detection of yellow head virus in shrimp.J Virol Methods. 2009 Dec;162(1-2):81-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.07.018. Epub 2009 Jul 29. J Virol Methods. 2009. PMID: 19646483 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse transcription-PCR assays for the differentiation of various US porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains.J Virol Methods. 2016 Aug;234:137-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.04.018. Epub 2016 Apr 28. J Virol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27134071 Free PMC article.
-
The taxonomy, host range and pathogenicity of coronaviruses and other viruses in the Nidovirales order.Anim Dis. 2021;1(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s44149-021-00005-9. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Anim Dis. 2021. PMID: 34778878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boonyaratpalin S., Supamattaya K., Kasornchandra J., Direkbusaracom S., Aekpanithanpong U., Cantanachookin C. Non-occluded baculo-like virus, the causative agent of yellow-head disease in the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) Fish Patho. 1993;l28:103–109.
-
- Callinan R.B., Jiang L., Smith P.T., Soowannayan C. Fatal, virus-associated peripheral neuropathy and retinopathy in farmed Penaeus monodon in eastern Australia. I. Pathol. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003;53:181–193. - PubMed
-
- Chantanachookin C., Boonyaratpalin S., Kasornchandra J., Sataporn D., Ekpanithanpong U., Supamataya K., Sriurairatana S., Flegel T.W. Histology and ultrastructure reveal a new granulomas-like virus in Penaeus monodon affected by yellow-head disease. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1993;17:145–157.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

