Cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression at the site of recent myocardial infarction: friend or foe?
- PMID: 15020525
- PMCID: PMC1768143
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2003.010280
Cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression at the site of recent myocardial infarction: friend or foe?
Abstract
Background: Cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) is induced in cardiomyocytes only in response to stress, such as ischaemia.
Objective: To assess COX-2 expression at the site of recent myocardial infarction.
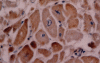
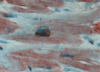
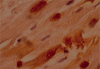
Methods: COX-2 expression was evaluated by specific immunostaining in cardiomyocytes from 23 subjects who died 10-60 days after acute myocardial infarction. The relation between COX-2 myocardial expression and apoptotic rate was investigated. Cardiomyocyte apoptotic rate was defined as the number of cells co-expressing in situ end labelling of DNA fragmentation (TUNEL) and immunostaining for activated caspase-3.
Results: COX-2 expression was found in cardiomyocytes at the site of infarction in nine of 23 cases (39%). It was associated with fivefold higher apoptotic rates (median 17.9% (interquartile range 11.0-25.4%) v 3.7% (0.6-12.8%); p = 0.016), and apoptotic rate increased progressively from mild to intense COX-2 staining (p for trend 0.009). COX-2 expression co-localised with TUNEL nuclear staining in myocytes, and there was a high concordance between COX-2 and hypoxia induced factor 1-alpha staining (78%, p = 0.021) and between COX-2 and bax (83%, p = 0.014). Subjects showing myocardial COX-2 expression were more likely to have enlarged hearts (p = 0.050), and intense COX-2 staining was strictly associated with symptomatic heart failure (p = 0.035).
Conclusions: COX-2 is expressed in cardiomyocytes in nearly 40% of cases at the site of recent acute myocardial infarction, even late after the index event. Its expression was associated with extremely high apoptotic rates. These findings suggest a potential cause-effect link between COX-2 expression and enhanced myocardial apoptosis in ischaemic cardiomyopathy.
Figures

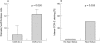
Similar articles
-
Infarct-related artery occlusion, tissue markers of ischaemia, and increased apoptosis in the peri-infarct viable myocardium.Eur Heart J. 2005 Oct;26(19):2039-45. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi419. Epub 2005 Jul 19. Eur Heart J. 2005. PMID: 16030061
-
Direct and indirect effects of aldosterone on cyclooxygenase-2 and interleukin-6 expression in rat cardiac cells in culture and after myocardial infarction.Endocrinology. 2004 Jul;145(7):3135-42. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1544. Epub 2004 Mar 24. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15044365
-
Inhibition of COX pathway in experimental myocardial infarction.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004 Jul;37(1):71-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2004.04.002. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15242737
-
Selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors and myocardial infarction: how strong is the link?Drug Saf. 2002;25(12):829-35. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200225120-00001. Drug Saf. 2002. PMID: 12241124 Review.
-
Regulation of cyclo-oxygenase-2.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2001 Oct;15(5):787-800. doi: 10.1053/bega.2001.0235. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11566041 Review.
Cited by
-
D-Tagatose Feeding Reduces the Risk of Sugar-Induced Exacerbation of Myocardial I/R Injury When Compared to Its Isomer Fructose.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 13;8:650962. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.650962. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33928123 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular tissue changes in early myocardial ischemia: from pathophysiology to the identification of new diagnostic markers.Int J Legal Med. 2018 Mar;132(2):425-438. doi: 10.1007/s00414-017-1750-z. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Int J Legal Med. 2018. PMID: 29362873 Review.
-
Cox-2 Negatively Affects the Protective Role of Propofol against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Induced Cardiomyocytes Apoptosis through Suppressing Akt Signaling.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jul 16;2019:7587451. doi: 10.1155/2019/7587451. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31380437 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid protects rodent hearts from ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase-derived PGD2 biosynthesis.J Clin Invest. 2009 Jun;119(6):1477-88. doi: 10.1172/JCI37413. Epub 2009 May 18. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19451694 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting inflammation: impact on atherothrombosis.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2014 Feb;7(1):9-18. doi: 10.1007/s12265-013-9523-7. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2014. PMID: 24327329 Review.
References
-
- Smith WL, Garavito RM, De Witt DL. Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases (cyclo-oxygenases)-1 and -2. J Biol Chem 1996;271:33157–60. - PubMed
-
- Shinmura K, Xuan YT, Tang XL, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase modulates cyclooxygenase-2 activity in the heart of conscious rabbits during the late phase of ischemic preconditioning. Circ Res 2002;90:602–8. - PubMed
-
- Wong SCY, Fukuchi M, Melnyk P, et al. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 and activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in myocardium of patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 1998;98:100–3. - PubMed
-
- Mani K, Kitsis RN. Myocyte apoptosis: programming ventricular remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41:761–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
