Inflammatory mediators in chronic heart failure: an overview
- PMID: 15020532
- PMCID: PMC1768165
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2002.007005
Inflammatory mediators in chronic heart failure: an overview
Figures


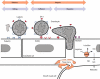
References
-
- Mann DL. Inflammatory mediators and the failing heart: past, present, and the foreseeable future. Circ Res 2002;91:988–98. ▸ Comprehensive up-to-date review of basic science issues in the context of cytokines in heart failure. - PubMed
-
- Tsutamoto T, Hisanaga T, Wada A, et al. Interleukin-6 spillover in the peripheral circulation increases with the severity of heart failure, and the high plasma level of interleukin-6 is an important prognostic predictor in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998;31:391–8. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Egerer KR, Volk HD, et al. Elevated soluble CD14 receptors and altered cytokines in chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 1997;79:1426–30. ▸ Original publication formulating the endotoxin hypothesis. - PubMed
-
- Genth-Zotz S, von Haehling S, Bolger AP, et al. Pathophysiologic quantities of endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha release in whole blood from patients with chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 2002;90:1226–30. ▸ First study to use very small—that is, pathophysiologically relevant—concentrations of LPS to induce pro-inflammatory cytokine production in CHF. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
