Chromatin-mediated restriction of nuclear factor 1/CTF binding in a repressed and hormone-activated promoter in vivo
- PMID: 15024090
- PMCID: PMC371135
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.7.3036-3047.2004
Chromatin-mediated restriction of nuclear factor 1/CTF binding in a repressed and hormone-activated promoter in vivo
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jun;24(12):5636
Abstract
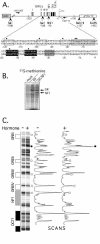
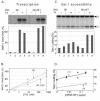
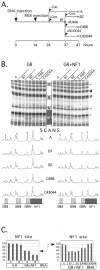
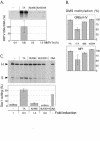
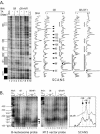
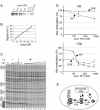
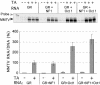
Mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) promoter-driven transcription is induced by glucocorticoid hormone via binding of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). The MMTV promoter also harbors a binding site for nuclear factor 1 (NF1). NF1 and GR were expressed in Xenopus oocytes; this revealed GR-NF1 cooperativity both in terms of DNA binding and chromatin remodeling but not transcription. A fraction of NF1 sites were occupied in a hormone-dependent fashion, but a significant and NF1 concentration-dependent fraction were constitutively bound. Activation of the MMTV promoter resulted in an approximately 50-fold increase in the NF1 accessibility for its DNA site. The hormone-dependent component of NF1 binding was dissociated by addition of a GR antagonist; however, the antagonist RU486, which supports partial GR-DNA binding, also maintained partial NF1 binding. Hence GR-NF1 cooperativity is independent of agonist-driven chromatin remodeling. NF1 induced the formation of a micrococcal-nuclease-resistant protein-DNA complex containing the DNA segment from -185 to -55, the MMTV enhanceosome. Coexpression of NF1 and Oct1 resulted in a significant stimulation of hormone-induced MMTV transcription and also in increased basal transcription. We propose that hormone-independent NF1 binding may be involved in maintaining transcriptional competence and establishment of tissue-specific gene networks.
Figures
References
-
- Almouzni, G., and A. P. Wolffe. 1993. Replication-coupled chromatin assembly is required for repression of basal transcription in vivo. Genes Dev. 7:2033-2047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
