Universal changes in biomarkers of coagulation and inflammation occur in patients with severe sepsis, regardless of causative micro-organism [ISRCTN74215569]
- PMID: 15025782
- PMCID: PMC420030
- DOI: 10.1186/cc2459
Universal changes in biomarkers of coagulation and inflammation occur in patients with severe sepsis, regardless of causative micro-organism [ISRCTN74215569]
Abstract
Introduction: PROWESS (Recombinant Human Activated Protein C Worldwide Evaluation in Severe Sepsis) was a phase III, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, multicenter trial conducted in patients with severe sepsis from 164 medical centers. Here we report data collected at study entry for 1690 patients and over the following 7 days for the 840 patients who received placebo (in addition to usual standard of care).
Methods: Nineteen biomarkers of coagulation activation, anticoagulation, fibrinolysis, endothelial injury, and inflammation were analyzed to determine the relationships between baseline values and their change over time, with 28-day survival, and type of infecting causative micro-organism.
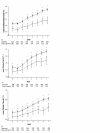
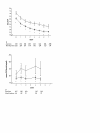
Results: Levels of 13 of the 19 biomarkers at baseline correlated with Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II scores, and nearly all patients exhibited coagulopathy, endothelial injury, and inflammation at baseline. At study entry, elevated D-dimer, thrombin-antithrombin complexes, IL-6, and prolonged prothrombin time were present in 99.7%, 95.5%, 98.5%, and 93.4% of patients, respectively. Markers of endothelial injury (soluble thrombomodulin) and deficient protein C, protein S, and antithrombin were apparent in 72%, 87.6%, 77.8%, and 81.7%, respectively. Impaired fibrinolysis (elevated plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) was observed in 44% of patients. During the first 7 days, increased prothrombin time (which is readily measurable in most clinical settings) was highly evident among patients who were not alive at 28 days.
Conclusion: Abnormalities in biomarkers of inflammation and coagulation were related to disease severity and mortality outcome in patients with severe sepsis. Coagulopathy and inflammation were universal host responses to infection in patients with severe sepsis, which were similar across causative micro-organism groups.
Figures



Comment in
-
Coagulation in sepsis: all bugs bite equally.Crit Care. 2004 Apr;8(2):99-100. doi: 10.1186/cc2816. Epub 2004 Feb 10. Crit Care. 2004. PMID: 15025767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Chest. 1992;101:1644–1655. - PubMed
-
- Corrigan JJ, Ray WL, May N. Changes in the blood coagulation system associated with septicemia. N Engl J Med. 1968;279:851–856. - PubMed
-
- ten Cate H, Timmerman JJ, Levi M. The pathophysiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82:713–717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

