gammadelta T-cell clones from intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes inhibit development of CTL responses ex vivo
- PMID: 15027900
- PMCID: PMC1782403
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0019-2805.2003.01793.x
gammadelta T-cell clones from intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes inhibit development of CTL responses ex vivo
Abstract
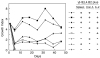
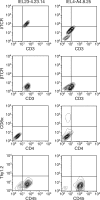
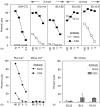
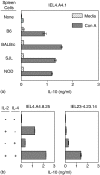
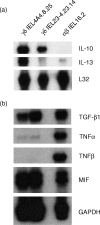
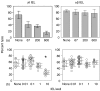
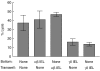
Oral administration of antigen induces a state of tolerance that is associated with activation of CD8+ T cells that can transfer unresponsiveness to naïve syngeneic hosts. These T cells are not lytic, but they inhibit development of antibody, CD4+ T helper cell, and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses upon adoptive transfer into naïve, syngeneic mice. In addition, we have shown that depletion of gammadelta T cells by injection of the anti-delta chain antibody (GL3) down modulates the expression of gammadelta T-cell receptor (TCR) and inhibits the induction of oral tolerance to ovalbumin. Oral administration of antigen also fails to induce tolerance in TCR delta-chain knockout mice suggesting that gammadelta T cells play a critical, active role in tolerance induced by orally administered antigen. To further study the contribution of gammadelta T cells to tolerance, murine gammadelta T cells were isolated from intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL) of the small intestine by stimulation with splenic filler cells, concanavalin A and growth factors. gammadelta IEL lines demonstrated lytic activity in a redirected lysis assay. gammadelta T-cell clones express different gammadelta TCR genes and secrete large amounts of interleukin (IL)-10, but little or no IL-2, IL-4, or interferon-gamma. gammadelta IEL clones expressed transforming growth factor-beta1 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor, as well as IL-10, mRNA. Moreover, gammadelta T-cell clones potently inhibited the generation of CTL responses by secreted molecules rather than by direct cell-to-cell contact.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of T-cell receptor-gammadelta+ cells in the intestinal epithelia of KN6 transgenic mice.Immunology. 2000 Sep;101(1):38-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00076.x. Immunology. 2000. PMID: 11012751 Free PMC article.
-
Unique properties of a cytotoxic CD4+CD8+ intraepithelial T-cell line established from the mouse intestinal epithelium.Microbiol Immunol. 1994;38(3):191-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1994.tb01764.x. Microbiol Immunol. 1994. PMID: 8078424
-
Immunoregulatory functions for murine intraepithelial lymphocytes: gamma/delta T cell receptor-positive (TCR+) T cells abrogate oral tolerance, while alpha/beta TCR+ T cells provide B cell help.J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):695-707. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.695. J Exp Med. 1992. PMID: 1531495 Free PMC article.
-
[T gamma-delta lymphocytes and their role in hypersensitivity processes in the digestive and respiratory mucosa].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2002 Sep-Oct;30(5):273-82. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2002. PMID: 12396962 Review. Spanish.
-
Role of gamma delta T cells in the regulation of mucosal IgA response and oral tolerance.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996 Feb 13;778:55-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb21114.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996. PMID: 8611016 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Vδ1γδT cells predominantly contributed to IL-17 production in the development of adult human post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun 30;21(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01722-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34193069 Free PMC article.
-
cis-Urocanic acid attenuates acute dextran sodium sulphate-induced intestinal inflammation.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 27;5(10):e13676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013676. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21060867 Free PMC article.
-
γδ T cells and their potential for immunotherapy.Int J Biol Sci. 2014 Jan 10;10(2):119-35. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7823. eCollection 2014. Int J Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24520210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging correlates with reduction in regulatory-type cytokines and T cells in the gut mucosa.Immunobiology. 2011 Oct;216(10):1085-93. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2011.05.007. Epub 2011 May 14. Immunobiology. 2011. PMID: 21676485 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of γδ T Cells in Different Pathogen Infections and Its Potential Clinical Application.J Immunol Res. 2018 Jul 10;2018:5081634. doi: 10.1155/2018/5081634. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30116753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mowat AM. Oral tolerance and regulation of immunity to dietary antigens. In: Ogra PL, Mestecky J, Lamm ME, Strober W, McGhee JR, Bienenstock J, editors. Handbook of Mucosal Immunology. New York: Academic Press, Inc; 1994. pp. 185–201.
-
- Ke Y, Kapp JA. Oral antigen inhibits priming of CD8+ CTL, CD4+ T cells and antibody responses while activating CD8+ suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1996;156:916–21. - PubMed
-
- Weiner HL, Friedman A, Miller A, et al. Oral Tolerance: immunologic mechanisms and treatment of animal and human organ-specific autoimmune disease by oral administration of autoantigens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:809–37. - PubMed
-
- Kato T, Owen RL. Structure and function of intestinal mucosal epithelium. In: Ogra PL, Mestecky J, Lamm ME, Strober W, McGhee JR, Bienenstock J, editors. Handbook of Mucosal Immunology. San Diego CA: Academic Press, Inc; 1994. pp. 11–26.
-
- Panja A, Mayer L. Diversity and function of antigen-presenting cells in mucosal tissues. In: Ogra PL, Mestecky J, Lamm ME, Strober W, McGhee JR, Bienenstock J, editors. Handbook of Mucosal Immunology. San Diego CA: Academic Press, Inc; 1994. pp. 177–84.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
