Neurohumoral stimulation in type-2-diabetes as an emerging disease concept
- PMID: 15028121
- PMCID: PMC406517
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-3-4
Neurohumoral stimulation in type-2-diabetes as an emerging disease concept
Abstract
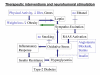
Neurohumoral stimulation comprising both autonomic-nervous-system dysfunction and activation of hormonal systems including the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) was found to be associated with Type-2-diabetes (T2D). Therapeutic strategies such as RAAS interference proved to be beneficial in both T2D treatment and prevention. In addition to an activated RAAS, hyperleptinemia in obesity, hyperinsulinemia in conditions of peripheral insulin resistance and overall oxidative stress in T2D represent known activators of the sympathetic component of the autonomic nervous system. Here, we hypothesize that sympathetic activation may cause peripheral insulin resistance defined as partial blocking of insulin effects on glucose uptake. Resulting hyperinsulinemia or hyperglycemia-related oxidative stress may further aggravate sympatho-excitation. This notion leads to a secondary hypothesis: sympathetic activation worsens from obesity towards insulin resistance, and further towards T2D. In this review, existing evidence relating to neurohumoral stimulation in T2D and consequences thereof, such as oxidative stress and inflammation, are discussed. The aim of this review is to provide a rationale for therapies, which are able to intercept neuroendocrine pathways in T2D and precursor states such as obesity.
Figures

References
-
- Cohn JN, Levine TB, Olivari MT, Garberg V, Lura D, Francis GS, Simon AB, Rector T. Plasma norepinephrine as a guide to prognosis in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1984;311:819–823. - PubMed
-
- Isnard R, Pousset F, Trochu J, Chafirovskaia O, Carayon A, Golmard J, Lechat P, Thomas D, Bouhour J, Komajda M. Prognostic value of neurohormonal activation and cardiopulmonary exercise testing in patients with chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2000;86:417–421. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(00)00957-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rodeheffer RJ, Lerman A, Heublein DM, Burnett JC. Increased plasma concentrations of endothelin in congestive heart failure in humans. Mayo Clin Proc. 1992;67:719–724. - PubMed
-
- Carnethon MR, Golden SH, Folsom AR, Haskell W, Liao D. Prospective investigation of autonomic nervous system function and the development of type 2 diabetes: the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities study, 1987–1998. Circulation. 2003;107:2190–2195. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000066324.74807.95. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

