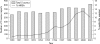Emergence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteraemia among children in England and Wales, 1990-2001
- PMID: 15033852
- PMCID: PMC1719863
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2003.028712
Emergence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteraemia among children in England and Wales, 1990-2001
Abstract
Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is now a major cause of adult bacteraemia. All reports of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia to the Health Protection Agency were analysed from 1990 to 2001. There were 376 cases of MRSA bacteraemia in children <15 years over this time. The proportion of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia due to MRSA increased steadily from 0.9% in 1990 to 13% in 2000. The proportion was higher in infants. MRSA bacteraemia is now a serious problem in children in England and Wales. More data on the risk factors for acquisition and spread of MRSA in children are required.
Figures
Comment in
-
MRSA: the problem reaches paediatrics.Arch Dis Child. 2004 Apr;89(4):297-8. doi: 10.1136/adc.2003.045534. Arch Dis Child. 2004. PMID: 15033832 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical