Beyond the diffusion limit: Water flow through the empty bacterial potassium channel
- PMID: 15034178
- PMCID: PMC387329
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0308309101
Beyond the diffusion limit: Water flow through the empty bacterial potassium channel
Abstract
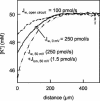
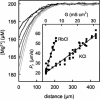
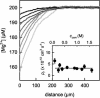
Water molecules are constrained to move with K+ ions through the narrow part of the Streptomyces lividans K+ channel because of the single-file nature of transport. In the presence of an osmotic gradient, a water molecule requires <10 ps to cross the purified protein reconstituted into planar bilayers. Rinsing K+ out of the channel, water may be 1,000 times faster than the fastest experimentally observed K+ ion and 20 times faster than the one-dimensional bulk diffusion of water. Both the anomalously high water mobility and its inhibition observed at high K+ concentrations are consistent with the view that liquid-vapor oscillations occur because of geometrical confinements of water in the selectivity filter. These oscillations, where the chain of molecules imbedded in the channel (the "liquid") cooperatively exits the channel, leaving behind a near vacuum (the "vapor"), thus far have only been discovered in hydrophobic nanopores by molecular dynamics simulations [Hummer, G., Rasaiah, J. C. & Noworyta, J. P. (2001) Nature 414, 188-190; and Beckstein, O. & Sansom, M. S. P. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 7063-7068].
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantum mechanical calculations of charge effects on gating the KcsA channel.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 May;1768(5):1218-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.01.021. Epub 2007 Feb 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17336921 Free PMC article.
-
Permeation of water through the KcsA K+ channel.Proteins. 2009 Feb 1;74(2):437-48. doi: 10.1002/prot.22163. Proteins. 2009. PMID: 18636474
-
Molecular dynamics study of the KcsA potassium channel.Biophys J. 1999 Nov;77(5):2502-16. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77086-4. Biophys J. 1999. PMID: 10545352 Free PMC article.
-
pH-dependent gating in the Streptomyces lividans K+ channel.Biochemistry. 1998 Mar 10;37(10):3229-36. doi: 10.1021/bi972997x. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9536962
-
Simulations of ion permeation through a potassium channel: molecular dynamics of KcsA in a phospholipid bilayer.Biophys J. 2000 Feb;78(2):557-70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76616-1. Biophys J. 2000. PMID: 10653771 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ion transport through membrane-spanning nanopores studied by molecular dynamics simulations and continuum electrostatics calculations.Biophys J. 2005 Oct;89(4):2222-34. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.065946. Epub 2005 Jul 8. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 16006629 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics simulation of water permeation through the alpha-hemolysin channel.J Biol Phys. 2016 Jan;42(1):133-46. doi: 10.1007/s10867-015-9396-x. Epub 2015 Aug 12. J Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 26264478 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical and simulation studies on voltage-gated sodium channels.Protein Cell. 2015 Jun;6(6):413-22. doi: 10.1007/s13238-015-0152-6. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Protein Cell. 2015. PMID: 25894089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PoreDesigner for tuning solute selectivity in a robust and highly permeable outer membrane pore.Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 10;9(1):3661. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06097-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30202038 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Conduction Mechanisms in Potassium Channels Revealed by Permeation Cycles.J Chem Theory Comput. 2023 May 9;19(9):2574-2589. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.3c00061. Epub 2023 Apr 11. J Chem Theory Comput. 2023. PMID: 37040262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou, Y., Morais-Cabral, J. H., Kaufman, A. & MacKinnon, R. (2001) Nature 414, 43–48. - PubMed
-
- Doyle, D. A., Morais, C. J., Pfuetzner, R. A., Kuo, A., Gulbis, J. M., Cohen, S. L., Chait, B. T. & MacKinnon, R. (1998) Science 280, 69–77. - PubMed
-
- Morais-Cabral, J. H., Zhou, Y. & MacKinnon, R. (2001) Nature 414, 37–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

