Intracellular transport of human lysosomal alpha-mannosidase and alpha-mannosidosis-related mutants
- PMID: 15035660
- PMCID: PMC1133862
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20031499
Intracellular transport of human lysosomal alpha-mannosidase and alpha-mannosidosis-related mutants
Abstract
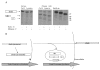
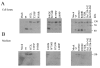
Human LAMAN (lysosomal a-mannosidase) was synthesized as a 120 kDa precursor in transfected COS cells [African-green-monkey kidney cells], which was partly secreted as a single-chain form and partly sorted to the lysosomes being subsequently cleaved into three peptides of 70, 40 and 15 kDa respectively. Both the secreted and the lysosomal forms contained endo H (endoglucosidase H)-resistant glycans, suggesting a common pathway through the trans-Golgi network. A fraction of LAMAN was retained intracellularly as a single-chain endo H-sensitive form, probably in the ER (endoplasmic reticulum). The inherited lack of LAMAN causes the autosomal recessive storage disease a-mannosidosis. To understand the biochemical consequences of the disease-causing mutations, 11 missense mutations and two in-frame deletions were introduced into human LAMAN cDNA by in vitro mutagenesis and the resulting proteins were expressed in COS cells. Some selected mutants were also expressed in Chinese-hamster ovary cells. T355P (Thr355Pro), P356R, W714R, R750W and L809P LAMANs as well as both deletion mutants were misfolded and arrested in the ER as inactive single-chain forms. Six of the mutants were transported to the lysosomes, either with less than 5% of normal specific activity (H72L, D196E/N and R220H LAMANs) or with more than 30% of normal specific activity (E402K LAMAN). F320L LAMAN resulted in much lower activity in Chinese-hamster ovary cells when compared with COS cells. Modelling into the three-dimensional structure revealed that the mutants with highly reduced specific activities contained substitutions of amino acids involved in the catalysis, either co-ordinating Zn2+ (His72 and Asp196), stabilizing the active-site nucleophile (Arg220) or positioning the active-site residue Asp319 (Phe320).
Figures




References
-
- DeGasperi R., al Daher S., Daniel P. F., Winchester B. G., Jeanloz R. W., Warren C. D. The substrate specificity of bovine and feline lysosomal α-D-mannosidases in relation to α-mannosidosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:16556–16563. - PubMed
-
- Aronson N. N., Kuranda M. J. Lysosomal degradation of Asn-linked glycoproteins. FASEB J. 1989;3:2615–2622. - PubMed
-
- Heikinheimo P., Helland R., Leiros H.-K., Karlsen S., Evjen G., Ravelli R., Schoen G., Ruigrok R., Tollersrud O. K., McSweeney S., et al. The structure of bovine lysosomal α-mannosidase suggests a novel mechanism for low pH activation. J. Mol. Biol. 2003;327:631–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

