A post-genomic approach to understanding sphingolipid metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 15037448
- PMCID: PMC4242313
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mch071
A post-genomic approach to understanding sphingolipid metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
Aims: To highlight the importance of sphingolipids and their metabolites in plant biology.
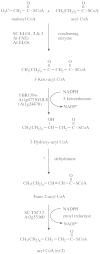
Scope: The completion of the arabidopsis genome provides a platform for the identification and functional characterization of genes involved in sphingolipid biosynthesis. Using the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as an experimental model, this review annotates arabidopsis open reading frames likely to be involved in sphingolipid metabolism. A number of these open reading frames have already been subject to functional characterization, though the majority still awaits investigation. Plant-specific aspects of sphingolipid biology (such as enhanced long chain base heterogeneity) are considered in the context of the emerging roles for these lipids in plant form and function.
Conclusions: Arabidopsis provides an excellent genetic and post-genomic model for the characterization of the roles of sphingolipids in higher plants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The essential nature of sphingolipids in plants as revealed by the functional identification and characterization of the Arabidopsis LCB1 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase.Plant Cell. 2006 Dec;18(12):3576-93. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.040774. Epub 2006 Dec 28. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 17194770 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipid long-chain base hydroxylation is important for growth and regulation of sphingolipid content and composition in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2008 Jul;20(7):1862-78. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.057851. Epub 2008 Jul 8. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18612100 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of sphingolipids in plants (and some of their functions).Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;688:249-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6741-1_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20919660 Review.
-
Characterization of an Arabidopsis cDNA encoding a subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase, the initial enzyme in sphingolipid biosynthesis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2001 Nov;42(11):1274-81. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pce165. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11726713
-
Yeast sphingolipids: recent developments in understanding biosynthesis, regulation, and function.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Mar;1771(3):421-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.08.005. Epub 2006 Aug 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 16997623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acyl-lipid metabolism.Arabidopsis Book. 2010;8:e0133. doi: 10.1199/tab.0133. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Arabidopsis Book. 2010. PMID: 22303259 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Arabidopsis Ceramide Synthases Differentially Affects Growth, Sphingolipid Metabolism, Programmed Cell Death, and Mycotoxin Resistance.Plant Physiol. 2015 Oct;169(2):1108-17. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00987. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26276842 Free PMC article.
-
Disruptions of the Arabidopsis Enoyl-CoA reductase gene reveal an essential role for very-long-chain fatty acid synthesis in cell expansion during plant morphogenesis.Plant Cell. 2005 May;17(5):1467-81. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.030155. Epub 2005 Apr 13. Plant Cell. 2005. PMID: 15829606 Free PMC article.
-
The Two Classes of Ceramide Synthases Play Different Roles in Plant Immunity and Cell Death.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 7;13:824585. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.824585. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35463421 Free PMC article.
-
GLUCOSAMINE INOSITOLPHOSPHORYLCERAMIDE TRANSFERASE1 (GINT1) Is a GlcNAc-Containing Glycosylinositol Phosphorylceramide Glycosyltransferase.Plant Physiol. 2018 Jul;177(3):938-952. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00396. Epub 2018 May 14. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29760197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BeaudoinF, Gable K, Sayanova O, Dunn T, Napier JA.2002. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene required for heterologous fatty acid elongase activity encodes a microsomal beta‐keto‐reductase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 277: 11481–11488. - PubMed
-
- BeckmannC, Rattke J, Sperling P, Heinz E, Boland W.2003. Stereochemistry of a bifunctional dihydroceramide delta 4‐desaturase/hydroxylase from Candida albicans; a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry 1: 2448–54. - PubMed
-
- BeelerT, Bacikova D, Gable K, Hopkins L, Johnson C, Slife H, Dunn T.1998. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae TSC10/YBR265w gene encoding 3‐ketosphinganine reductase is identified in a screen for temperature‐sensitive suppressors of the Ca2+‐sensitive csg2D mutant. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273: 30688–30694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

