Cervical radiculopathy: open study on percutaneous periradicular foraminal steroid infiltration performed under CT control in 30 patients
- PMID: 15037470
- PMCID: PMC8158560
Cervical radiculopathy: open study on percutaneous periradicular foraminal steroid infiltration performed under CT control in 30 patients
Abstract
Background and purpose: Cervical radiculopathy is a common entity that can become unremitting, seriously disrupting the patient's work and social activities. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the feasibility, tolerance, and efficacy of transforaminal periganglionic steroid infiltration under CT control.
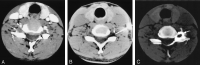
Methods: Thirty patients with cervical radiculopathy, despite at least 1 month of appropriate medical treatment, underwent percutaneous periradicular foraminal steroid infiltration under CT control. Sixteen patients had foraminal degenerative stenosis, and 14 patients had disk herniation. The intensity of radicular pain was scored on an analogic visual scale (AVS). Pain relief was classified as excellent when the pain had diminished by 75% or more; good, by 50%-74%; fair by 25%-49%; or poor, by less than 25%. The patients were followed up at 2 weeks and at 6 months.
Results: No local complications occurred after the procedure. The mean AVS pain scores were 6.5 points before the procedure and 3.3 points 2 weeks after, with significant pain relief (P <.001). Pain relief was excellent in 11 patients (37%) and good in seven patients (23%). There was no rebound of pain at the 6-month follow-up. The duration of symptoms before infiltration and the intensity and cause of radiculalgia were not predictive of radicular pain relief.
Conclusion: Intraforaminal cervical infiltration produced substantial sustained pain relief, whatever the cause of the radiculalgia. The CT approach ensures the safety of vital structures and allows the precise injection of a steroid specifically targeted to the ganglia.
Figures
Comment in
-
Back surgery begets back surgery.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004 Mar;25(3):354-5. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004. PMID: 15037455 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Smith MD. Cervical radiculopathy: causes and surgical treatment. Minn Med 1995;78:28–30, 42–45 - PubMed
-
- Horal J. The clinical appearance of low back disorders in the city of Gothenburg, Sweden: comparisons of incapacitated probands with matched controls. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 1969;118:1–109 - PubMed
-
- Ellenberg MR, Honet JC, Treanor WJ. Cervical radiculopathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1994;75:342–352 - PubMed
-
- Sampath P, Bendebba M, Davis JD, Ducker T. Outcome in patients with cervical radiculopathy: prospective, multicenter study with independent clinical review. Spine 1999;24:591–597 - PubMed
-
- Stav A, Ovadia L, Sternberg A, Kaadan M, Weksler N. Cervical epidural steroid injection for cervicobrachialgia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1993;37:562–566 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
