Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA6 is required for maintenance of transcriptional gene silencing and determines nuclear organization of rDNA repeats
- PMID: 15037732
- PMCID: PMC412874
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.018754
Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA6 is required for maintenance of transcriptional gene silencing and determines nuclear organization of rDNA repeats
Abstract
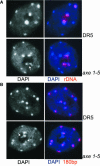
Histone acetylation and deacetylation are connected with transcriptional activation and silencing in many eukaryotic organisms. Gene families for enzymes that accomplish these modifications show a surprising multiplicity in sequence and expression levels, suggesting a high specificity for different targets. We show that mutations in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) HDA6, a putative class I histone deacetylase gene, result in loss of transcriptional silencing from several repetitive transgenic and endogenous templates. Surprisingly, total levels of histone H4 acetylation are only slightly affected, whereas significant hyperacetylation is restricted to the nucleolus organizer regions that contain the rDNA repeats. This switch coincides with an increase of histone 3 methylation at Lys residue 4, a modified DNA methylation pattern, and a concomitant decondensation of the chromatin. These results indicate that HDA6 might play a role in regulating activity of rRNA genes, and this control might be functionally linked to silencing of other repetitive templates and to its previously assigned role in RNA-directed DNA methylation.
Figures





References
-
- Ahringer, J. (2000). NuRD and SIN3 histone deacetylase complexes in development. Trends Genet. 16, 351–356. - PubMed
-
- Amedeo, P., Habu, Y., Afsar, K., Mittelsten Scheid, O., and Paszkowski, J. (2000). Disruption of the plant gene MOM releases transcriptional silencing of methylated genes. Nature 405, 203–206. - PubMed
-
- Berger, S.L. (2002). Histone modifications in transcriptional regulation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12, 142–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

