Immunoglobulin-mediated agglutination of and biofilm formation by Escherichia coli K-12 require the type 1 pilus fiber
- PMID: 15039312
- PMCID: PMC375160
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.4.1929-1938.2004
Immunoglobulin-mediated agglutination of and biofilm formation by Escherichia coli K-12 require the type 1 pilus fiber
Abstract
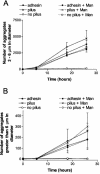
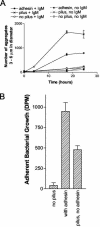
The binding of human secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA), the primary immunoglobulin in the gut, to Escherichia coli is thought to be dependent on type 1 pili. Type 1 pili are filamentous bacterial surface attachment organelles comprised principally of a single protein, the product of the fimA gene. A minor component of the pilus fiber (the product of the fimH gene, termed the adhesin) mediates attachment to a variety of host cell molecules in a mannose inhibitable interaction that has been extensively described. We found that the aggregation of E. coli K-12 by human secretory IgA (SIgA) was dependent on the presence of the pilus fiber, even in the absence of the mannose specific adhesin or in the presence of 25 mM alpha-CH(3)Man. The presence of pilus without adhesin also facilitated SIgA-mediated biofilm formation on polystyrene, although biofilm formation was stronger in the presence of the adhesin. IgM also mediated aggregation and biofilm formation in a manner dependent on pili with or without adhesin. These findings indicate that the pilus fiber, even in the absence of the adhesin, may play a role in biologically important processes. Under conditions in which E. coli was agglutinated by SIgA, the binding of SIgA to E. coli was not increased by the presence of the pili, with or without adhesin. This observation suggests that the pili, with or without adhesin, affect factors such as cell surface rigidity or electrostatic repulsion, which can affect agglutination but which do not necessarily determine the level of bound immunoglobulin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biofilm formation in a hydrodynamic environment by novel fimh variants and ramifications for virulence.Infect Immun. 2001 Mar;69(3):1322-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.3.1322-1328.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11179294 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory IgA and mucin-mediated biofilm formation by environmental strains of Escherichia coli: role of type 1 pili.Mol Immunol. 2006 Feb;43(4):378-87. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2005.02.013. Mol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16310051
-
A Newly Identified Group of P-like (PL) Fimbria Genes from Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) Encode Distinct Adhesin Subunits and Mediate Adherence to Host Cells.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jul 12;88(13):e0142121. doi: 10.1128/aem.01421-21. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35758695 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone-assisted assembly and molecular architecture of adhesive pili.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:383-415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.002123. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 1683764 Review.
-
Pili with strong attachments: Gram-positive bacteria do it differently.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Oct;62(2):320-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05279.x. Epub 2006 Sep 15. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16978260 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Secretory Immunoglobulin A in Host-Microbiota Interactions in the Gut Ecosystem.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 2;13:880484. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.880484. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35722300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro biofilm formation of commensal and pathogenic Escherichia coli strains: impact of environmental and genetic factors.J Bacteriol. 2006 May;188(10):3572-81. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.10.3572-3581.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16672611 Free PMC article.
-
Upstream migration of Xylella fastidiosa via pilus-driven twitching motility.J Bacteriol. 2005 Aug;187(16):5560-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5560-5567.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16077100 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiome and breast-feeding: Implications for early immune development.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Sep;150(3):523-534. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.07.014. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36075638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Pre-diagnostic Antibody Responses to Escherichia coli and Bacteroides fragilis Toxin Proteins with Colorectal Cancer in a European Cohort.Gut Microbes. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1-14. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1903825. Gut Microbes. 2021. PMID: 33874856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baenziger, J., and S. Kornfeld. 1974. Structure of the carbohydrate units of IgA1 immunoglobulin. I. Composition, glycopeptide isolation, and structure of the asparagine-linked oligosaccharide units. J. Biol. Chem. 249:7260-7269. - PubMed
-
- Baenziger, J., and S. Kornfeld. 1974. Structure of the carbohydrate units of IgA1 immunoglobulin. II. Structure of the O-glycosidically linked oligosaccharide units. J. Biol. Chem. 249:7270-7281. - PubMed
-
- Blattner, F. R., G. Plunkett III, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. Collado-Vides, J. D. Glasner, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davis, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453-1474. - PubMed
-
- Bloch, C. A., B. A. Stocker, and P. E. Orndorff. 1992. A key role for type 1 pili in enterobacterial communicability. Mol. Microbiol. 6:697-701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

