The Arabidopsis cytochrome P450 CYP707A encodes ABA 8'-hydroxylases: key enzymes in ABA catabolism
- PMID: 15044947
- PMCID: PMC391058
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600121
The Arabidopsis cytochrome P450 CYP707A encodes ABA 8'-hydroxylases: key enzymes in ABA catabolism
Abstract
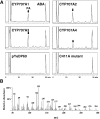
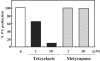
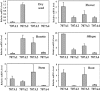
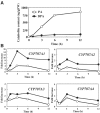
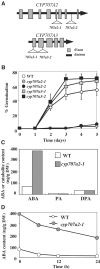
The hormonal action of abscisic acid (ABA) in plants is controlled by the precise balance between its biosynthesis and catabolism. In plants, ABA 8'-hydroxylation is thought to play a predominant role in ABA catabolism. ABA 8'-hydroxylase was shown to be a cytochrome P450 (P450); however, its corresponding gene had not been identified. Through phylogenetic and DNA microarray analyses during seed imbibition, the candidate genes for this enzyme were narrowed down from 272 Arabidopsis P450 genes. These candidate genes were functionally expressed in yeast to reveal that members of the CYP707A family, CYP707A1-CYP707A4, encode ABA 8'-hydroxylases. Expression analyses revealed that CYP707A2 is responsible for the rapid decrease in ABA level during seed imbibition. During drought stress conditions, all CYP707A genes were upregulated, and upon rehydration a significant increase in mRNA level was observed. Consistent with the expression analyses, cyp707a2 mutants exhibited hyperdormancy in seeds and accumulated six-fold greater ABA content than wild type. These results demonstrate that CYP707A family genes play a major regulatory role in controlling the level of ABA in plants.
Figures


References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Horn E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid M, Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Asami T, Sekimata K, Wang JM, Yoneyama K, Takeuchi Y, Yoshida S (1999) Preparation of (±)-[1,2-13C2]abscisic acid for use as a stable and pure internal standard. J Chem Res (Synop) 11: 658–659
-
- Balsevich JJ, Abrams SR, Lamb N, König WA (1994b) Identification of unnatural phaseic acid as a metabolite derived from exogenously added (−)-abscisic acid in a maize cell suspension culture. Phytochemistry 36: 647–650
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

