Architecture and assembly of mammalian H/ACA small nucleolar and telomerase ribonucleoproteins
- PMID: 15044956
- PMCID: PMC394235
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600181
Architecture and assembly of mammalian H/ACA small nucleolar and telomerase ribonucleoproteins
Abstract
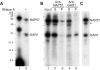
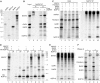
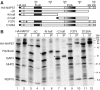
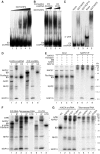
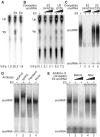
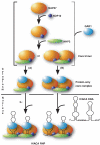
Mammalian H/ACA small nucleolar RNAs and telomerase RNA share common sequence and secondary structure motifs that form ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs) with the same four core proteins, NAP57 (also dyskerin or in yeast Cbf5p), GAR1, NHP2, and NOP10. The assembly and molecular interactions of the components of H/ACA RNPs are unknown. Using in vitro transcription/translation in combination with immunoprecipitation of core proteins, UV-crosslinking, and electrophoretic mobility shift assays, we demonstrate the following. NOP10 associates with NAP57 as a prerequisite for NHP2 binding. Although NHP2 on its own binds RNA nonspecifically, this NAP57-NOP10-NHP2 core trimer specifically recognizes H/ACA RNAs. GAR1 associates independently with NAP57 near the pseudouridylase core of mature H/ACA RNPs. In contrast to other RNPs whose assembly is initiated by protein-RNA interactions, the four H/ACA core proteins form a protein-only particle that associates with H/ACA RNAs. Nonetheless, functional H/ACA snoRNPs assembled in cytosolic extracts are stable and do not exchange their RNA components, suggesting that new particle formation requires de novo synthesis.
Figures
References
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV (1999) Novel predicted RNA-binding domains associated with the translation machinery. J Mol Evol 48: 291–302 - PubMed
-
- Bachellerie JP, Cavaille J (1997) Guiding ribose methylation of rRNA. Trends Biochem Sci 22: 257–261 - PubMed
-
- Bagni C, Lapeyre B (1998) Gar1p binds to the small nucleolar RNAs snR10 and snR30 in vitro through a nontypical RNA binding element. J Biol Chem 273: 10868–10873 - PubMed
-
- Bonnerot C, Pintard L, Lutfalla G (2003) Functional redundancy of Spb1p and a snR52-dependent mechanism for the 2′-O-ribose methylation of a conserved rRNA position in yeast. Mol Cell 12: 1309–1315 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

