CD4-independent infection of astrocytes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1: requirement for the human mannose receptor
- PMID: 15047828
- PMCID: PMC374297
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.8.4120-4133.2004
CD4-independent infection of astrocytes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1: requirement for the human mannose receptor
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(13):7288-9
Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection occurs in the central nervous system and causes a variety of neurobehavioral and neuropathological disorders. Both microglia, the residential macrophages in the brain, and astrocytes are susceptible to HIV-1 infection. Unlike microglia that express and utilize CD4 and chemokine coreceptors CCR5 and CCR3 for HIV-1 infection, astrocytes fail to express CD4. Astrocytes express several chemokine coreceptors; however, the involvement of these receptors in astrocyte HIV-1 infection appears to be insignificant. In the present study using an expression cloning strategy, the cDNA for the human mannose receptor (hMR) was found to be essential for CD4-independent HIV-1 infectivity. Ectopic expression of functional hMR rendered U87.MG astrocytic cells susceptible to HIV-1 infection, whereas anti-hMR serum and hMR-specific siRNA blocked HIV-1 infection in human primary astrocytes. In agreement with these findings, hMR bound to HIV-1 virions via the abundant and highly mannosylated sugar moieties of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 in a Ca(2+)-dependent fashion. Moreover, hMR-mediated HIV-1 infection was dependent upon endocytic trafficking as assessed by transmission electron microscopy, as well as inhibition of viral entry by endosomo- and lysosomotropic drugs. Taken together, these results demonstrate the direct involvement of hMR in HIV-1 infection of astrocytes and suggest that HIV-1 interaction with hMR plays an important role in HIV-1 neuropathogenesis.
Figures

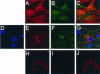

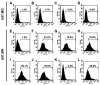
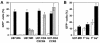
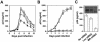
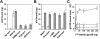
 ) grown in a 96-well plate were prechilled on ice for 30 min, followed by the addition of 100 ng of gagp24 HIV-GFP viruses pseudotyped with VSV-G, HXB2, YU-2, and 89.6 envelope proteins, or without envelope protein (no env) were then added. The cells were allowed to incubate with the viruses for an additional 30 min. After 30 min, the viruses were removed and the cells were washed extensively with prechilled regular culture medium. The cells were then lysed with a 1% NP-40-containing buffer, and the lysates were processed to determine HIV-1 binding by using the p24 ELISA kit. (B) Inhibition of HIV-1 binding to human mannose receptor by hMR antibody and ligand antagonists. U87.MR cells were incubated with HIV-GFP viruses pseudotyped with HXB2 envelope protein (□), or VSV-G envelope protein (
) grown in a 96-well plate were prechilled on ice for 30 min, followed by the addition of 100 ng of gagp24 HIV-GFP viruses pseudotyped with VSV-G, HXB2, YU-2, and 89.6 envelope proteins, or without envelope protein (no env) were then added. The cells were allowed to incubate with the viruses for an additional 30 min. After 30 min, the viruses were removed and the cells were washed extensively with prechilled regular culture medium. The cells were then lysed with a 1% NP-40-containing buffer, and the lysates were processed to determine HIV-1 binding by using the p24 ELISA kit. (B) Inhibition of HIV-1 binding to human mannose receptor by hMR antibody and ligand antagonists. U87.MR cells were incubated with HIV-GFP viruses pseudotyped with HXB2 envelope protein (□), or VSV-G envelope protein ( ), as stated above, in the presence of goat preimmune serum (1:50), goat anti-hMR serum (1:50), and 3 mg of yeast mannan or
), as stated above, in the presence of goat preimmune serum (1:50), goat anti-hMR serum (1:50), and 3 mg of yeast mannan or 
 ) envelope protein in the presence of different reagents, and HIV-1 infection was determined as described above. For VSV-G pseudotyped virus infection, only 1/20 of the lysates was used for Luc enzymatic activity assay, whereas only one-fifth of the lysates was used for HXB2 pseudotyped HIV-1 infection of U87.CD4.CXCR4 cells.
) envelope protein in the presence of different reagents, and HIV-1 infection was determined as described above. For VSV-G pseudotyped virus infection, only 1/20 of the lysates was used for Luc enzymatic activity assay, whereas only one-fifth of the lysates was used for HXB2 pseudotyped HIV-1 infection of U87.CD4.CXCR4 cells.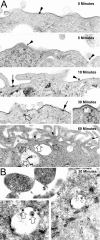
References
-
- Achord, D. T., F. E. Brot, and W. S. Sly. 1977. Inhibition of the rat clearance system for agalacto-orosomucoid by yeast mannans and by mannose. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 77:409-415. - PubMed
-
- Berger, E. A., P. M. Murphy, and J. M. Farber. 1999. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:657-700. - PubMed
-
- Biller, M., A. Bolmstedt, A. Hemming, and S. Olofsson. 1998. Simplified procedure for fractionation and structural characterisation of complex mixtures of N-linked glycans, released from HIV-1 gp120 and other highly glycosylated viral proteins. J. Virol. Methods 76:87-100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

