Microfluidics in biotechnology
- PMID: 15056390
- PMCID: PMC411055
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-2-2
Microfluidics in biotechnology
Abstract
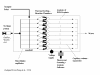
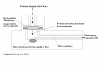
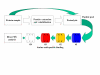
Microfluidics enables biotechnological processes to proceed on a scale (microns) at which physical processes such as osmotic movement, electrophoretic-motility and surface interactions become enhanced. At the microscale sample volumes and assay times are reduced, and procedural costs are lowered. The versatility of microfluidic devices allows interfacing with current methods and technologies. Microfluidics has been applied to DNA analysis methods and shown to accelerate DNA microarray assay hybridisation times. The linking of microfluidics to protein analysis techologies, e.g. mass spectrometry, enables picomole amounts of peptide to be analysed within a controlled micro-environment. The flexibility of microfluidics will facilitate its exploitation in assay development across multiple biotechnological disciplines.
Figures
References
-
- Clark J, Shevchuk T, Swiderski PM, Dabur R, Crocitto LE, Buryanov YI, Smith SS. Mobility-shift analysis with microfluidics chips. Biotechniques. 2003;35:548–554. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Vaidya B, Farquar HD, Stryjewski W, Hammer RP, McCarley RL, Soper SA, Cheng YW, Barany F. Microarrays assembled in microfluidic chips fabricated from poly(methyl methacrylate) for the detection of low-abundant DNA mutations. Anal Chem. 2003;75:1130–1140. doi: 10.1021/ac020683w. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

