Extracellular signal-regulated kinases regulate dendritic growth in rat sympathetic neurons
- PMID: 15056710
- PMCID: PMC6730016
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3286-03.2004
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases regulate dendritic growth in rat sympathetic neurons
Abstract
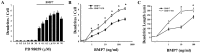
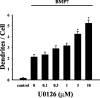
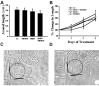
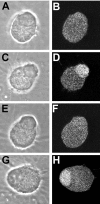
NGF activates several signaling cascades in sympathetic neurons. We examined how activation of one of these cascades, the ERK/MAP (extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein) kinase pathway, affects dendritic growth in these cells. Dendritic growth was induced by exposure to NGF and BMP-7 (bone morphogenetic protein-7). Exposure to NGF increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Unexpectedly, two MEK (MAP kinase kinase) inhibitors (PD 98059 and U 0126) enhanced dendritic growth, and a ligand, basic FGF, that activates the ERK pathway inhibited the growth of these processes. The enhancement of dendritic growth by PD 98059 was associated with an increase in the number of axo-dendritic synapses, and it appeared to represent a specific morphogenic effect because neither axonal growth nor cell survival was affected. In addition, increased dendritic growth was not observed after exposure to inhibitors of other signaling pathways, including the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor LY 294002. Dendritic growth was also increased in cells transfected with dominant-negative mutants of MEK1 and ERK2 but not with dominant-negative mutants of MEK5 and ERK5, suggesting that ERK1/2 is the primary mediator of this effect. Exposure to BMP-7 induces nuclear translocation of Smad1 (Sma- and Mad-related protein 1), and PD 98059 treatment potentiated nuclear accumulation of Smad-1 induced by BMP-7 in sympathetic neurons, suggesting a direct enhancement of BMP signaling in cells treated with an MEK inhibitor. These observations indicate that one of the signaling cascades activated by NGF can act in an antagonistic manner in sympathetic neurons and reduce the dendritic growth induced by other NGF-sensitive pathways.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Dendritic growth induced by BMP-7 requires Smad1 and proteasome activity.J Neurobiol. 2001 Aug;48(2):120-30. J Neurobiol. 2001. PMID: 11438941
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-5 (BMP-5) promotes dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons.BMC Neurosci. 2001;2:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-2-12. Epub 2001 Sep 11. BMC Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11580864 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-7 stimulates initial dendritic growth in sympathetic neurons through an intracellular fibroblast growth factor signaling pathway.J Neurochem. 2002 Jan;80(1):54-63. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-3042.2001.00657.x. J Neurochem. 2002. PMID: 11796743
-
MAPK signalling: ERK5 versus ERK1/2.EMBO Rep. 2006 Aug;7(8):782-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400755. EMBO Rep. 2006. PMID: 16880823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transduction of bone morphogenetic protein receptors.Cell Signal. 2004 Mar;16(3):291-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2003.08.011. Cell Signal. 2004. PMID: 14687659 Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal gut Bifidobacterium breve modifies fetal brain metabolism in germ-free mice.Mol Metab. 2024 Oct;88:102004. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.102004. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39127167 Free PMC article.
-
The novel GTPase Rit differentially regulates axonal and dendritic growth.J Neurosci. 2007 Apr 25;27(17):4725-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5633-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17460085 Free PMC article.
-
Rit subfamily small GTPases: regulators in neuronal differentiation and survival.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2060-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of NMDA receptors by neuregulin signaling in prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2005 May 18;25(20):4974-84. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1086-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15901778 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the Clinical and Molecular Characterization of Noonan Syndrome and Other RASopathies: A Retrospective Study and Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 9;26(8):3515. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083515. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams JP, Sweatt JD (2002) Molecular psychology: roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42: 135–163. - PubMed
-
- Atwal JK, Massie B, Miller FD, Kaplan DR (2000) The TrkB-Shc site signals neuronal survival and local axon growth via MEK and P13-kinase. Neuron 27: 265–277. - PubMed
-
- Baker RE, Dijkhuizen PA, Van Pelt J, Verhaagen J (1998) Growth of pyramidal, but not non-pyramidal, dendrites in long-term organotypic explants of neonatal rat neocortex chronically exposed to neurotrophin-3. Eur J Neurosci 10: 1037–1044. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin C, Sasek CA, Zigmond RE (1991) Evidence that some preganglionic sympathetic neurons in the rat contain vasoactive intestinal peptideor peptide histidine isoleucine amide-like immunoreactivities. Neuroscience 40: 175–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
