VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis in inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage recruitment
- PMID: 15057311
- PMCID: PMC379325
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20465
VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis in inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage recruitment
Abstract
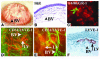
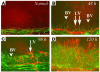
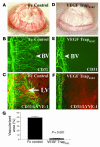
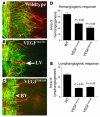
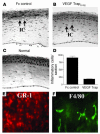
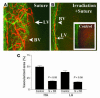
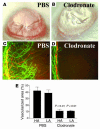
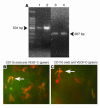
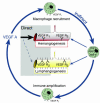
Lymphangiogenesis, an important initial step in tumor metastasis and transplant sensitization, is mediated by the action of VEGF-C and -D on VEGFR3. In contrast, VEGF-A binds VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 and is an essential hemangiogenic factor. We re-evaluated the potential role of VEGF-A in lymphangiogenesis using a novel model in which both lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis are induced in the normally avascular cornea. Administration of VEGF Trap, a receptor-based fusion protein that binds and neutralizes VEGF-A but not VEGF-C or -D, completely inhibited both hemangiogenesis and the outgrowth of LYVE-1(+) lymphatic vessels following injury. Furthermore, both lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis were significantly reduced in mice transgenic for VEGF-A(164/164) or VEGF-A(188/188) (each of which expresses only one of the three principle VEGF-A isoforms). Because VEGF-A is chemotactic for macrophages and we demonstrate here that macrophages in inflamed corneas release lymphangiogenic VEGF-C/VEGF-D, we evaluated the possibility that macrophage recruitment plays a role in VEGF-A-mediated lymphangiogenesis. Either systemic depletion of all bone marrow-derived cells (by irradiation) or local depletion of macrophages in the cornea (using clodronate liposomes) prior to injury significantly inhibited both hemangiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. We conclude that VEGF-A recruitment of monocytes/macrophages plays a crucial role in inducing inflammatory neovascularization by supplying/amplifying signals essential for pathological hemangiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.
Figures
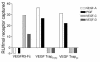
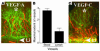
References
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat. Med. 1995;1:27–31. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2003;9:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Kerbel R, Folkman J. Clinical translation of angiogenesis inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:727–739. - PubMed
-
- Stacker SA, Achen MG, Jussila L, Baldwin ME, Alitalo K. Lymphangiogenesis and cancer metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:573–583. - PubMed
-
- He Y, et al. Suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 2002;94:819–825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

