The synovial proteome: analysis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes
- PMID: 15059280
- PMCID: PMC400437
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1153
The synovial proteome: analysis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes
Abstract
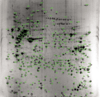
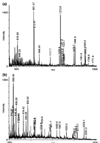
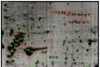
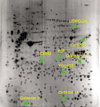
The present studies were initiated to determine the protein expression patterns of fibroblast-like synovial (FLS) cells derived from the synovia of rheumatoid arthritis patients. The cellular proteins were separated by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the in-gel digested proteins were analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. A total of 368 spots were examined and 254 identifications were made. The studies identified a number of proteins that have been implicated in the normal or pathological FLS function (e.g. uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase, galectin 1 and galectin 3) or that have been characterized as potential autoantigens in rheumatoid arthritis (e.g. BiP, colligin, HC gp-39). A novel uncharacterized protein product of chromosome 19 open reading frame 10 was also detected as an apparently major component of FLS cells. These results demonstrate the utility of high-content proteomic approaches in the analysis of FLS composition.
Figures
References
-
- Yamanishi Y, Firestein GS. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: the role of synoviocytes. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2001;27:355–371. - PubMed
-
- Zimmermann T, Kunisch E, Pfeiffer R, Hirth A, Stahl HD, Sack U, Laube A, Liesaus E, Roth A, Palombo-Kinne E, Emmrich F, Kinne RW. Isolation and characterization of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts from primary culture–primary culture cells markedly differ from fourth-passage cells. Arthritis Res. 2001;3:72–76. doi: 10.1186/ar142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

