Regulatory potential scores from genome-wide three-way alignments of human, mouse, and rat
- PMID: 15060013
- PMCID: PMC383316
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1976004
Regulatory potential scores from genome-wide three-way alignments of human, mouse, and rat
Abstract
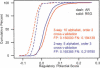
We generalize the computation of the Regulatory Potential (RP) score from two-way alignments of human and mouse to three-way alignments of human, mouse, and rat. This requires overcoming technical challenges that arise because the complexity of the models underlying the score increases exponentially with the number of species. Despite the close evolutionary proximity of rat to mouse, we find that adding the rat sequence increases our ability to predict genomic sites that regulate gene transcription. A variant of the RP scoring scheme that accounts for local variation in neutral mutational patterns further improves our predictions.
Figures
References
-
- Berman, B.P., Nibu, Y., Pfeiffer, B.D., Tomancak, P., Celniker, S.E., Levine, M., Rubin, G.M., and Eisen, M.B. 2002. Exploiting transcription factor binding site clustering to identify cis-regulatory modules involved in pattern formation in the Drosophila genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99: 757-762. - PMC - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- http://bio.cse.psu.edu/mousegroup/Reg_annotations; Repository of functional regulatory elements, Penn State University.
-
- http://www.bx.psu.edu; Center for Comparative Genomics and Bioinformatics, Penn State University.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
