Molecular analysis of high-copy insertion sites in maize
- PMID: 15060129
- PMCID: PMC390377
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnh052
Molecular analysis of high-copy insertion sites in maize
Abstract
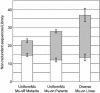
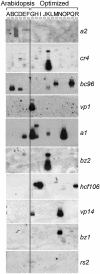
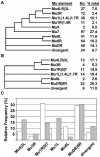
High-copy transposon mutagenesis is an effective tool for creating gene disruptions in maize. In order to molecularly define transposon-induced disruptions on a genome-wide scale, we optimized TAIL-PCR to amplify genomic DNA flanking maize Robertson's Mutator insertions. Sample sequencing from 43 Mutator stocks and the W22 inbred line identified 676 non-redundant insertions, and only a small fraction of the flanking sequences showed significant similarity to maize repetitive sequences. We further designed and tested 79 arbitrary primers to identify 12 primers that amplify all Mutator insertions within a DNA sample at 3.1-fold redundancy. Importantly, the products are of sufficient size to use as substrates or probes for hybridization-based identification of gene disruptions. Our adaptation simplifies previously published TAIL-PCR protocols and should be transferable to other high-copy insertional mutagens.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and isolation of Mu-flanking fragments from maize.J Genet Genomics. 2008 Apr;35(4):207-13. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60029-6. J Genet Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18439977
-
Use of Illumina sequencing to identify transposon insertions underlying mutant phenotypes in high-copy Mutator lines of maize.Plant J. 2010 Jul 1;63(1):167-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04231.x. Epub 2010 Apr 19. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 20409008
-
High-throughput TAIL-PCR as a tool to identify DNA flanking insertions.Methods Mol Biol. 2003;236:241-72. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-413-1:241. Methods Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14501069
-
Progress in maize gene discovery: a project update.Funct Integr Genomics. 2003 Mar;3(1-2):25-32. doi: 10.1007/s10142-002-0078-y. Epub 2002 Oct 1. Funct Integr Genomics. 2003. PMID: 12590340 Review.
-
Functional genomics in Arabidopsis: large-scale insertional mutagenesis complements the genome sequencing project.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2000 Apr;11(2):157-61. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(00)00075-6. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2000. PMID: 10753770 Review.
Cited by
-
Embracing native diversity to enhance the maximum quantum efficiency of photosystem II in maize.Plant Physiol. 2024 Dec 24;197(1):kiae670. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae670. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39711175 Free PMC article.
-
Production of transgenic strawberries by temporary immersion bioreactor system and verification by TAIL-PCR.BMC Biotechnol. 2007 Feb 19;7:11. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-7-11. BMC Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17309794 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the maize gravitropism gene lazy plant1 by a transposon-tagging genome resequencing strategy.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 31;9(1):e87053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087053. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498020 Free PMC article.
-
Wristwatch PCR: A Versatile and Efficient Genome Walking Strategy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 12;10:792848. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.792848. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35497369 Free PMC article.
-
Production of viable gametes without meiosis in maize deficient for an ARGONAUTE protein.Plant Cell. 2011 Feb;23(2):443-58. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.079020. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21325139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coelho P.S., Kumar,A. and Snyder,M. (2000) Genome-wide mutant collections: toolboxes for functional genomics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 3, 309–315. - PubMed
-
- Parinov S. and Sundaresan,V. (2000) Functional genomics in Arabidopsis: large-scale insertional mutagenesis complements the genome sequencing project. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 11, 157–161. - PubMed
-
- Wendel J.F. (2000) Genome evolution in polyploids. Plant Mol. Biol., 42, 225–249. - PubMed
-
- Shoemaker D.D., Lashkari,D.A., Morris,D., Mittman,M. and Davis,R.W. (1996) Quantitative phenotypic analysis of yeast deletion mutants using a highly parallel molecular bar-coding strategy. Nature Genet., 14, 450–456. - PubMed

