Calcineurin: a central controller of signalling in eukaryotes
- PMID: 15060569
- PMCID: PMC1299038
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400133
Calcineurin: a central controller of signalling in eukaryotes
Abstract
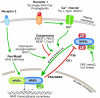
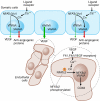
Workshop on the Calcium/Calcineurin/NFAT Pathway: Regulation and Function
Figures


References
-
- Chuvpilo S et al. (2002) Autoregulation of NFATc1/A expression facilitates effector T cells to escape from rapid apoptosis. Immunity 16: 881–895 - PubMed
-
- Graef IA, Mermelstein PG, Stankunas K, Neilson JR, Deisseroth K, Tsien RW, Crabtree GR (1999) L-type calcium channels and GSK-3 regulate the activity of NF-ATc4 in hippocampal neurons. Nature 401: 703–708 - PubMed
-
- Graef IA, Chen F, Chen L, Kuo A, Crabtree GR (2001) Signals transduced by Ca(2+)/calcineurin and NFATc3/c4 pattern the developing vasculature. Cell 105: 863–875 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

