Ethylene insensitivity does not increase leaf area or relative growth rate in Arabidopsis, Nicotiana tabacum, and Petunia x hybrida
- PMID: 15064382
- PMCID: PMC419903
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.034389
Ethylene insensitivity does not increase leaf area or relative growth rate in Arabidopsis, Nicotiana tabacum, and Petunia x hybrida
Abstract
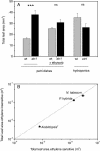
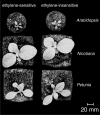
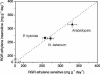
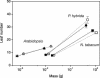
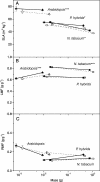
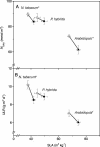
The plant hormone ethylene plays a role in various growth related processes. In this detailed study of the vegetative growth of Arabidopsis, Nicotiana tabacum, and Petunia x hybrida plants, we show that ethylene insensitivity does not result in an increased total leaf area or relative growth rate (RGR) under optimal growth conditions. When grown in semiclosed containers, leaf area of ethylene-insensitive plants was larger compared to the wild type. This effect was caused by a buildup of ethylene inside these containers, which inhibited the growth of wild-type plants. Ethylene-insensitive Arabidopsis and N. tabacum plants had a lower biomass, which was mainly the result of a smaller seed mass. RGR of vegetative plants was not affected by ethylene insensitivity, but the underlying components of RGR differed; specific leaf area (leaf area per unit leaf mass) was higher, and unit leaf rate (growth rate per unit leaf area) was lower. The latter was a result of a slower rate of photosynthesis per unit leaf area in the ethylene-insensitive plants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ethylene insensitivity results in down-regulation of rubisco expression and photosynthetic capacity in tobacco.Plant Physiol. 2007 Jul;144(3):1305-15. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.099762. Epub 2007 May 25. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17535822 Free PMC article.
-
The central role of PhEIN2 in ethylene responses throughout plant development in petunia.Plant Physiol. 2004 Oct;136(2):2900-12. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.046979. Epub 2004 Oct 1. Plant Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15466231 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylene Exerts Species-Specific and Age-Dependent Control of Photosynthesis.Plant Physiol. 2018 Apr;176(4):2601-2612. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01706. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29438047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The application of ethephon (an ethylene releaser) increases growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen accumulation in mustard (Brassica juncea L.) under high nitrogen levels.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008 Sep;10(5):534-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2008.00054.x. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008. PMID: 18761492
-
Ethylene and Hormonal Cross Talk in Vegetative Growth and Development.Plant Physiol. 2015 Sep;169(1):61-72. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00724. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26232489 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Variation of enzyme activities and metabolite levels in 24 Arabidopsis accessions growing in carbon-limited conditions.Plant Physiol. 2006 Dec;142(4):1574-88. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.086629. Epub 2006 Oct 27. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17085515 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylene Supplementation Combined with Split Application of Nitrogen and Sulfur Protects Salt-Inhibited Photosynthesis through Optimization of Proline Metabolism and Antioxidant System in Mustard (Brassica juncea L.).Plants (Basel). 2021 Jun 27;10(7):1303. doi: 10.3390/plants10071303. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199061 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroplasts at the Crossroad of Photosynthesis, Pathogen Infection and Plant Defense.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 5;19(12):3900. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123900. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30563149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of ethylene pretreatment on tomato plant responses to salt, drought, and waterlogging stress.Plant Direct. 2023 Nov 17;7(11):e548. doi: 10.1002/pld3.548. eCollection 2023 Nov. Plant Direct. 2023. PMID: 38028648 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylene Role in Plant Growth, Development and Senescence: Interaction with Other Phytohormones.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Apr 4;8:475. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00475. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28421102 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abeles FB, Morgan PW, Saltveit ME (1992) Ethylene in Plant Biology. Academic Press, New York
-
- Atkin OK, Botman B, Lambers H (1996) The causes of inherently slow growth in alpine plants: an analysis based on the underlying carbon economies of alpine and lowland Poa species. Funct Ecol 10: 698–707
-
- Bleecker AB, Estelle MA, Somerville C, Kende H (1988) Insensitivity to ethylene conferred by a dominant mutation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 141: 1086–1087 - PubMed
-
- Brenner ML, Cheikh N (1995) Hormones in photosynthate partitioning and seed filling. In PJ Davies, ed, Plant Hormones. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 649–670
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

