A comparison of sequential sampling models for two-choice reaction time
- PMID: 15065913
- PMCID: PMC1440925
- DOI: 10.1037/0033-295X.111.2.333
A comparison of sequential sampling models for two-choice reaction time
Abstract
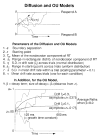
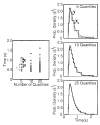
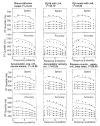
The authors evaluated 4 sequential sampling models for 2-choice decisions--the Wiener diffusion, Ornstein-Uhlenbeck (OU) diffusion, accumulator, and Poisson counter models--by fitting them to the response time (RT) distributions and accuracy data from 3 experiments. Each of the models was augmented with assumptions of variability across trials in the rate of accumulation of evidence from stimuli, the values of response criteria, and the value of base RT across trials. Although there was substantial model mimicry, empirical conditions were identified under which the models make discriminably different predictions. The best accounts of the data were provided by the Wiener diffusion model, the OU model with small-to-moderate decay, and the accumulator model with long-tailed (exponential) distributions of criteria, although the last was unable to produce error RTs shorter than correct RTs. The relationship between these models and 3 recent, neurally inspired models was also examined.
Figures







References
-
- Ashby FG. A biased random walk model of two choice reaction times. Journal of Mathematical Psychology. 1983;27:277–297.
-
- Audley RJ, Mercer A. The relation between decision time and the relative response frequency in a blue-green discrimination. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology. 1968;21:183–192. - PubMed
-
- Audley RJ, Pike AR. Some alternate stochastic models of choice. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology. 1965;18:207–225. - PubMed
-
- Buonocore A, Giorno V, Nobile AG, Ricciardi L. On the two-boundary first-crossing-time problem for diffusion processes. Journal of Applied Probability. 1990;27:102–114.
-
- Burbeck SL, Luce RD. Evidence from auditory simple reaction times for both change and level detectors. Perception & Psychophysics. 1982;32:117–133. - PubMed

