Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics and epidemiological significance of ctx+ strains of Vibrio cholerae isolated from seafood in Malaysia
- PMID: 15066786
- PMCID: PMC383156
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.4.1964-1972.2004
Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics and epidemiological significance of ctx+ strains of Vibrio cholerae isolated from seafood in Malaysia
Abstract
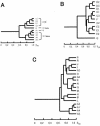
Of 97 strains of Vibrio cholerae isolated from various seafoods in Malaysia in 1998 and 1999, 20 strains carried the ctx gene and produced cholera toxin. Fourteen, one, and five of these toxigenic strains belonged to the O139, O1 Ogawa, and rough serotypes, respectively. The rough strains had the rfb gene of the O1 serotype. The toxigenic strains varied in their biochemical characteristics, the amount of cholera toxin produced, their antibiograms, and the presence or absence of the pTLC plasmid sequence. DNA fingerprinting analysis by arbitrarily primed PCR, ribotyping, and a pulsed-field gel electrophoresis method classified the toxigenic strains into 3, 7, and 10 types, respectively. The relatedness of these toxigenic strains to clinical strains isolated in other countries and from international travelers was examined by using a dendrogram constructed from the pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles. The results of the examination of the antibiogram and the possession of the toxin-linked cryptic plasmid were consistent with the dendrogram-based relatedness: the O139 strains isolated from Malaysian seafoods could be separated into two groups that appear to have been introduced from the Bengal area independently. The rough strains of Malaysian seafood origin formed one group and belonged to a cluster unique to the Thailand-Malaysia-Laos region, and this group may have persisted in this area for a long period. The single O1 Ogawa strain detected in Malaysian seafood appears to have an origin and route of introduction different from those of the O139 and the rough strains.
Figures

References
-
- Albert, M. J., M. Neira, and Y. Motarjemi. 1997. The role of food in epidemiology of cholera. World Health Stat. Q. 50:111-118. - PubMed
-
- Albert, M. J., A. K. Siddique, M. S. Islam, A. S. G. Faruque, M. Ansaruzzaman, S. M. Faruque, and R. B. Sack. 1993. Large outbreak of clinical cholera due to Vibrio cholerae non-O1 in Bangladesh. Lancet 341:704. - PubMed
-
- Basu, A., A. K. Mukhopadhyay, P. Garg, S. Chakraborty, T. Ramamurthy, S. Yamasaki, Y. Takeda, and G. B. Nair. 2000. Diversity in the arrangement of the CTX prophages in classical strains of Vibrio cholerae O1. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 182:35-40. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, A. W., W. M. M. Kirby, J. C. Sherris, and M. Turck. 1966. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45:493-496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

