Differential regulation of calcium homeostasis in adenocarcinoma cell line A549 and its Taxol-resistant subclone
- PMID: 15066902
- PMCID: PMC1574945
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705755
Differential regulation of calcium homeostasis in adenocarcinoma cell line A549 and its Taxol-resistant subclone
Abstract
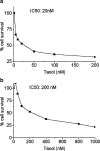
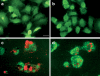
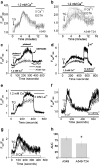
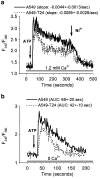
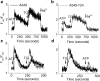
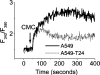
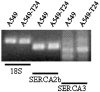
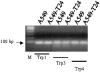
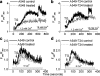
Drug resistance is a fundamental problem in cancer chemotherapy. Intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+](i)) may play a role in the development of chemoresistance. We investigated the regulatory role of [Ca2+](i) in Taxol resistance in the non-small-cell lung cancer cell line A549 and its chemoresistant subclone A549-T24. Measurement of cytosolic calcium ([Ca2+](c)) in single cells and cell populations revealed similar levels of basal calcium in the two cell lines. However, a reduced response to thapsigargin (a sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) inhibitor) in A549-T24 cells compared to the parent cell line suggested a lower ER Ca2+ content in these cells. mRNA expression of SERCA2b and SERCA3, major Ca2+ pumps involved in ER Ca2+ homeostasis, did not significantly differ between the two cell lines, as revealed by RT-PCR. An altered calcium influx pathway in the Taxol-resistant cell line was observed. Modulation of the ER calcium pools using CMC (4-chloro-m-cresol) and ATP revealed lower ryanodine receptor (RyR) and IP(3) receptor (IP(3)R)-sensitive Ca2+ stores in the chemoresistant cell line. Western blot and RT-PCR studies suggested that A549-T24 cells expressed higher levels of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and the calcium-binding protein sorcin, respectively, in comparison to the parent cell line. Both of these proteins have been previously implicated in chemoresistance, in part, due to their ability to modulate[Ca2+](i). These results suggest that altered intracellular calcium homeostasis may contribute to the Taxol-resistant phenotype.
Figures
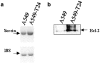

References
-
- BERRIDGE M.J., LIPP P., BOOTMAN M.D. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- BISWAS R.S., CHA H.J., HARDWICK J.M., SRIVASTAVA R.K. Inhibition of drug-induced Fas ligand transcription and apoptosis by Bcl-XL. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2001;225:7–20. - PubMed
-
- BLAGOSKLONNY M.V., FOJO T. Molecular effects of paclitaxel: myths and reality (a critical review) Int. J. Cancer. 1999;83:151–156. - PubMed
-
- BROUGH G.H., WU S., CIOFFI D., MOORE T.M., LI M., DEAN N., STEVENS T. Contribution of endogenously expressed Trp1 to a Ca2+-selective, store-operated Ca2+ entry pathway. Faseb. J. 2001;15:1727–1738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

