Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 15067033
- PMCID: PMC2211881
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20031579
Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis
Abstract
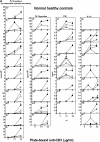
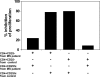
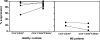
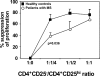
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells contribute to the maintenance of peripheral tolerance by active suppression because their deletion causes spontaneous autoimmune diseases in mice. Human CD4+ regulatory T cells expressing high levels of CD25 are suppressive in vitro and mimic the activity of murine CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory disease thought to be mediated by T cells recognizing myelin protein peptides. We hypothesized that altered functions of CD4+CD25hi regulatory T cells play a role in the breakdown of immunologic self-tolerance in patients with MS. Here, we report a significant decrease in the effector function of CD4+CD25hi regulatory T cells from peripheral blood of patients with MS as compared with healthy donors. Differences were also apparent in single cell cloning experiments in which the cloning frequency of CD4+CD25hi T cells was significantly reduced in patients as compared with normal controls. These data are the first to demonstrate alterations of CD4+CD25hi regulatory T cell function in patients with MS.
Figures



References
-
- Ota, K., M. Matsui, E.L. Milford, G.A. Mackin, H.L. Weiner, and D.A. Hafler. 1990. T-cell recognition of an immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 346:183–187. - PubMed
-
- Kappler, J.W., N. Roehm, and P. Marrack. 1987. T cell tolerance by clonal elimination in the thymus. Cell. 49:273–280. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi, S. 2000. Regulatory T cells: key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell. 101:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Shevach, E.M., R.S. McHugh, C.A. Piccirillo, and A.M. Thornton. 2001. Control of T-cell activation by CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells. Immunol. Rev. 182:58–67. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi, S., K. Fukuma, K. Kuribayashi, and T. Masuda. 1985. Organ-specific autoimmune diseases induced in mice by elimination of T cell subset. I. Evidence for the active participation of T cells in natural self-tolerance; deficit of a T cell subset as a possible cause of autoimmune disease. J. Exp. Med. 161:72–87. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

