Regulation of alternative RNA splicing by exon definition and exon sequences in viral and mammalian gene expression
- PMID: 15067211
- PMCID: PMC2442652
- DOI: 10.1007/BF02254432
Regulation of alternative RNA splicing by exon definition and exon sequences in viral and mammalian gene expression
Erratum in
- J Biomed Sci. 2004 Jul-Aug;11(4):538
Abstract
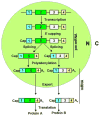
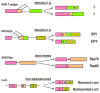
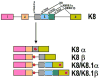
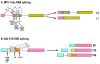
Intron removal from a pre-mRNA by RNA splicing was once thought to be controlled mainly by intron splicing signals. However, viral and other eukaryotic RNA exon sequences have recently been found to regulate RNA splicing, polyadenylation, export, and nonsense-mediated RNA decay in addition to their coding function. Regulation of alternative RNA splicing by exon sequences is largely attributable to the presence of two major cis-acting elements in the regulated exons, the exonic splicing enhancer (ESE) and the suppressor or silencer (ESS). Two types of ESEs have been verified from more than 50 genes or exons: purine-rich ESEs, which are the more common, and non-purine-rich ESEs. In contrast, the sequences of ESSs identified in approximately 20 genes or exons are highly diverse and show little similarity to each other. Through interactions with cellular splicing factors, an ESE or ESS determines whether or not a regulated splice site, usually an upstream 3' splice site, will be used for RNA splicing. However, how these elements function precisely in selecting a regulated splice site is only partially understood. The balance between positive and negative regulation of splice site selection likely depends on the cis-element's identity and changes in cellular splicing factors under physiological or pathological conditions.
Copyright 2004 National Science Council, ROC and S. Karger AG, Basel
Figures
References
-
- Akusjarvi G, Stevenin J. Remodelling of the host cell RNA splicing machinery during an adenovirus infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003;272:253–286. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AK, Lam YW, Steen H, Mann M, Lamond AI. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Aznarez I, Chan EM, Zielenski J, Blencowe BJ, Tsui LC. Characterization of disease-associated mutations affecting an exonic splicing enhancer and two cryptic splice sites in exon 13 of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:2031–2040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
