Mutation of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta inhibits Pkhd1 gene expression and produces renal cysts in mice
- PMID: 15067314
- PMCID: PMC362119
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20083
Mutation of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta inhibits Pkhd1 gene expression and produces renal cysts in mice
Abstract
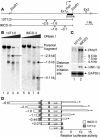
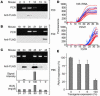
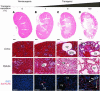
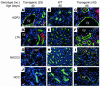
Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta (HNF-1beta) is a Pit-1, Oct-1/2, UNC-86 (POU)/homeodomain-containing transcription factor that regulates tissue-specific gene expression in the liver, kidney, and other organs. Humans with autosomal dominant mutations of HNF-1beta develop maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 5 (MODY5) and congenital cystic abnormalities of the kidney. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) is an inherited cystic disorder that produces renal failure in infants and children and is caused by mutations of PKHD1. The proximal promoter of the mouse Pkhd1 gene contains an evolutionarily conserved HNF-1-binding site that is located near a region of deoxyribonuclease hypersensitivity. HNF-1beta and the structurally related HNF-1alpha bind specifically to the Pkhd1 promoter and stimulate gene transcription. Mutations of the HNF-1 site or expression of a dominant-negative HNF-1beta mutant inhibit Pkhd1 promoter activity in transfected cells. Transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative HNF-1beta mutant under the control of a kidney-specific promoter develop renal cysts, similarly to humans with MODY5. Pkhd1 transcripts are absent in the cells lining the cysts but are present in morphologically normal surrounding tubules. These studies identify a link between two cystic disease genes, HNF1beta (MODY5) and PKHD1 (ARPKD). HNF-1beta directly regulates the transcription of Pkhd1, and inhibition of PKHD1 gene expression may contribute to the formation of renal cysts in humans with MODY5.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta (HNF-1beta) C-terminal domain in Pkhd1 (ARPKD) gene transcription and renal cystogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 18;280(11):10578-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414121200. Epub 2005 Jan 12. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15647252
-
Roles of HNF-1beta in kidney development and congenital cystic diseases.Kidney Int. 2005 Nov;68(5):1944-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00625.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 16221171 Review.
-
Regulation of kidney-specific Ksp-cadherin gene promoter by hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002 Oct;283(4):F839-51. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00128.2002. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12217876
-
Tissue-specific regulation of the mouse Pkhd1 (ARPKD) gene promoter.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Aug 1;307(3):F356-68. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00422.2013. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24899057 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of HNF-1β in kidney (patho)physiology.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Aug;34(8):1325-1335. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-3990-7. Epub 2018 Jul 1. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 29961928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and role of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 2 in the regulation of Na+/H+ exchanger 3 in the mammalian kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Dec;299(6):F1496-506. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00075.2010. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20926631 Free PMC article.
-
HNF1B mutations associate with hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 May;20(5):1123-31. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008060633. Epub 2009 Apr 23. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19389850 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-shock inducible Cre strains to study organogenesis in transgenic Xenopus laevis.Transgenic Res. 2009 Aug;18(4):595-605. doi: 10.1007/s11248-009-9253-4. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Transgenic Res. 2009. PMID: 19266305
-
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young as a model for elucidating the multifactorial origin of type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Investig. 2018 Jul;9(4):704-712. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12812. Epub 2018 Mar 23. J Diabetes Investig. 2018. PMID: 29406598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of vesicoureteral reflux and congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract.Investig Clin Urol. 2017 Jun;58(Suppl 1):S4-S13. doi: 10.4111/icu.2017.58.S1.S4. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Investig Clin Urol. 2017. PMID: 28612055 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pontoglio M. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1, a transcription factor at the crossroads of glucose homeostasis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000;11(Suppl. 16):S140–S143. - PubMed
-
- Mendel DB, Hansen LP, Graves MK, Conley PB, Crabtree GR. HNF-1α and HNF-1β (vHNF-1) share dimerization and homeo domains, but not activation domains, and form heterodimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991;5:1042–1056. - PubMed
-
- Barbacci E, et al. Variant hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 is required for visceral endoderm specification. Development. 1999;126:4795–4805. - PubMed
-
- Coffinier C, Barra J, Babinet C, Yaniv M. Expression of the vHNF1/HNF1β homeoprotein gene during mouse organogenesis. Mech. Dev. 1999;89:211–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

