Survivin antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 15069710
- PMCID: PMC4656345
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1121
Survivin antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of transfected survivin antisense oligonucleotide (ASODN) on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells.
Methods: The authors designed ASODNs targeting different regions of survivin mRNA, including surviving ASODN1, ASODN2 and ASODN3. ASODNs were transfected into gastric cancer cell line SGC 7901, cell growth was detected by MTT assay. Cells exposed to the potent oligonucleotide were also examined for apoptosis induction by FCM and fluorescence microscopy. Semiquantitive RT-PCR and Western blot examinations were carried for expression of survivin mRNA and protein.
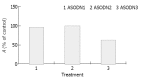
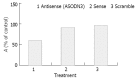
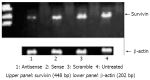
Results: ASODN3 caused a statistically significant reduction of cell viability to 60.6% (+/-2.9%) (P<0.01), while ASODN1 and ASODN2 had no such changes (P>0.05). The cell growth was also significantly inhibited by ASODN3, compared with reversal and scrambled sequence. A significant loss of survivin mRNA was presented in ASODN3 treated cells and this was not seen in treatment with sense ODN or scramble ODN. Protein level was significantly decreased 48 h after survivin ASODN trasfected by approximately 2-fold decrease compared with untreated controls. However, ASODN3 did not induce significant apoptosis response until 48 h after transfection (P>0.05).
Conclusion: ASODN3, which targets translation initiation part, can be identified as a most potent antisense compound. Srvivin ASODN3 may provide a novel approach to therapy of gastric cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Reed JC. Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2941–2953. - PubMed
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteins--suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999;13:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med. 1997;3:917–921. - PubMed
-
- Altieri DC, Marchisio PC. Survivin apoptosis: an interloper between cell death and cell proliferation in cancer. Lab Invest. 1999;79:1327–1333. - PubMed
-
- Lu CD, Altieri DC, Tanigawa N. Expression of a novel antiapoptosis gene, survivin, correlated with tumor cell apoptosis and p53 accumulation in gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998;58:1808–1812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

