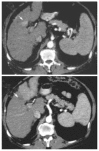
Rapid progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after Radiofrequency Ablation
- PMID: 15069713
- PMCID: PMC4656348
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1137
Rapid progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after Radiofrequency Ablation
Abstract
Aim: To report the results of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in cirrhotic patients and to describe the treatment related complications (mainly the rapid intrahepatic neoplastic progression).
Methods: Eighty-seven consecutive cirrhotic patients with 104 HCC (mean diameter 3.9 cm, 1.3 SD) were submitted to RFA between January 1998 and June 2003. In all cases RFA was performed with percutaneous approach under ultrasound guidance using expandable electrode needles. Treatment efficacy (necrosis and recurrence) was estimated with dual phase computed tomography (CT) and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level.
Results: Complete necrosis rate after single or multiple treatment was 100%, 87.7% and 57.1% in HCC smaller than 3 cm, between 3 and 5 cm and larger than 5 cm respectively (P=0.02). Seventeen lesions of 88(19.3%) developed local recurrence after complete necrosis during a mean follow up of 19.2 mo. There were no treatment-related deaths in 130 procedures and major complications occurred in 8 patients (6.1 %). In 4 patients, although complete local necrosis was achieved, we observed rapid intrahepatic neoplastic progression after treatment. Risk factors for rapid neoplastic progression were high preoperative AFP values and location of the tumor near segmental portal branches.
Conclusion: RFA is an effective treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma smaller than 5 cm with complete necrosis in more than 80% of lesions. Patients with elevated AFP levels and tumors located near the main portal branch are at risk for rapid neoplastic progression after RFA. Further studies are necessary to evaluate the incidence and pathogenesis of this underestimated complication.
Figures
References
-
- Simonetti RG, Liberati A, Angiolini C, Pagliaro L. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Ann Oncol. 1997;8:117–136. - PubMed
-
- Schafer DF, Sorrell MF. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 1999;353:1253–1257. - PubMed
-
- Farinati F, Rinaldi M, Gianni S, Naccarato R. How should patients with hepatocellular carcinoma be staged? Validation of a new prognostic system. Cancer. 2000;89:2266–2273. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A, Vilana R, Ayuso Mdel C, Sala M, Brú C, Rodés J, Bruix J. Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology. 1999;29:62–67. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Llovet JM. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002;35:519–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical