Construction of prokaryotic expression system of 2 148-bp fragment from cagA gene and detection of cagA gene, CagA protein in Helicobacter pylori isolates and its antibody in sera of patients
- PMID: 15069723
- PMCID: PMC4656358
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1183
Construction of prokaryotic expression system of 2 148-bp fragment from cagA gene and detection of cagA gene, CagA protein in Helicobacter pylori isolates and its antibody in sera of patients
Abstract
Aim: To construct a prokaryotic expression system of a Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) cagA gene fragment and establish enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for detecting CagA and its antibody, so as to understand the manner in which the infection of CagA-expressing H pylori (CagA(+) H pylori) isolates cause diseases.
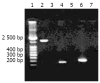
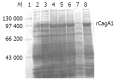
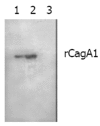
Methods: H pylori strains in gastric biopsy specimens from 156 patients with positive results in rapid urease test were isolated. PCR was used to detect the frequency of cagA gene in the 109 H pylori isolates and to amplify a 2 148-bp fragment (cagA1) of cagA gene from a clinical strain Y06. A prokaryotic expression system of cagA1 gene was constructed, and the expression of the target recombinant protein (rCagA1) was examined by SDS-PAGE. Western blotting and immunodiffusion assay were employed to determine the immunoreactivity and antigenicity of rCagA1, respectively. Two ELISAs were established to detect CagA expression in 109 H pylori isolates and the presence of CagA antibody in the corresponding patients' sera, and the correlations between infection with CagA(+) H pylori and gastritis as well as peptic ulcer were analyzed.
Results: Of all the clinical specimens obtained, 80.8% (126/156) were found to have H pylori isolates and 97.2% of the isolates (106/109) were positive for cagA gene. In comparison with the reported data, the cloned cagA1 fragment possessed 94.83% and 93.30% homologies with the nucleotide and putative amino acid sequences, respectively. The output of rCagA1 produced by the constructed recombinant prokaryotic expression system was approximately 30% of the total bacterial protein. rCagA1 was able to bind to the commercial antibody against the whole-cells of H pylori and to induce the immunized rabbits to produce antibody with an immunodiffusion titer of 1:4. A proportion as high as 92.6% of the H pylori isolates (101/109) expressed CagA and 88.1% of the patients' serum samples (96/109) were CagA antibody-positive. The percentage of CagA(+) H pylori strains (97.9%) isolated from the biopsy specimens of peptic ulcer appeared to be higher than that from gastritis (88.5%), but the difference was not statistically significant (chi (2)=3.48, P>0.05).
Conclusion: rCagA1 produced by the prokaryotic expression system constructed in this study possesses good immunoreactivity and antigenicity, and the established ELISAs can be used to detect CagA of H pylori and its antibody. H pylori isolates show high frequencies of cagA gene and CagA expression, but the infections by CagA(+) H pylori strains are not the most decisive factors to cause gastric diseases.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

