Identification of a dehydrogenase acting on D-2-hydroxyglutarate
- PMID: 15070399
- PMCID: PMC1133759
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20031933
Identification of a dehydrogenase acting on D-2-hydroxyglutarate
Abstract
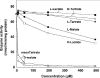
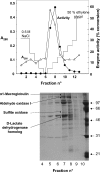
Extracts of frozen rat liver were found to catalyse the formation of 3H2O from DL-2-hydroxy[2-3H]glutarate. Three peaks of enzyme activities were observed on separation by chromatography on DEAE-Sepharose. The first and second peaks corresponded to an enzyme acting on L-2-hydroxyglutarate and the third peak corresponded to an enzyme acting on D-2-hydroxyglutarate, as indicated by competitive inhibition of the detritiation of the racemic radioactive compound by the unlabelled L- and D-isomers respectively. The enzyme acting on the D-form was further characterized. It was independent of NAD or NADP and it converted D-2-hydroxyglutarate into a-ketoglutarate, transferring electrons to artificial electron acceptors. It also oxidized D-lactate, D-malate and meso-tartrate and was stimulated by Zn2+, Co2+ and Mn2+, but not by Mg2+ or Ca2+. Subcellular fractionation indicated that it was present in the mitochondrial fraction. The enzyme was further purified by chromatography on Blue Trisacryl and phenyl-Sepharose, up to a stage where only a few bands were still visible by SDS/PAGE. Among the four candidate polypeptides that were identified by MS, one corresponded to a predicted mitochondrial protein homologous with FAD-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase. The corresponding human protein was expressed in HEK-293 cells and it was shown to catalyse the detritiation of DL-2-hydroxy[2-3H]glutarate with similar properties as the purified rat enzyme.
Figures




References
-
- Chalmers R. A., Lawson A. M., Watts R. W., Tavill A. S., Kamerling J. P., Hey E., Ogilvie D. D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: case report and biochemical studies. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1980;3:11–15. - PubMed
-
- van der Knaap M. S., Jakobs C., Hoffmann G. F., Duran M., Muntau A. C., Schweitzer S., Kelley R. I., Parrot-Roulaud F., Amiel J., de Lonlay P., et al. D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: further clinical delineation. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1999;22:404–413. - PubMed
-
- Lindahl G., Lindstedt G., Lindstedt S. Metabolism of 2-amino-5-hydroxyadipic acid in the rat. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1967;119:347–352. - PubMed
-
- Wanders R. J., Mooyer P. D-2-hydroxyglutaric acidaemia: identification of a new enzyme, D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, localized in mitochondria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1995;18:194–196. - PubMed
-
- Tubbs P. K. Effects of metal-complexing agents on mitochondrial D-α-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1960;3:513–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

