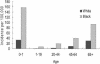Incidence of bloodstream infections due to Candida species and in vitro susceptibilities of isolates collected from 1998 to 2000 in a population-based active surveillance program
- PMID: 15070998
- PMCID: PMC387610
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.4.1519-1527.2004
Incidence of bloodstream infections due to Candida species and in vitro susceptibilities of isolates collected from 1998 to 2000 in a population-based active surveillance program
Abstract
To determine the incidence of Candida bloodstream infections (BSI) and antifungal drug resistance, population-based active laboratory surveillance was conducted from October 1998 through September 2000 in two areas of the United States (Baltimore, Md., and the state of Connecticut; combined population, 4.7 million). A total of 1,143 cases were detected, for an average adjusted annual incidence of 10 per 100,000 population or 1.5 per 10,000 hospital days. In 28% of patients, Candida BSI developed prior to or on the day of admission; only 36% of patients were in an intensive care unit at the time of diagnosis. No fewer than 78% of patients had a central catheter in place at the time of diagnosis, and 50% had undergone surgery within the previous 3 months. Candida albicans comprised 45% of the isolates, followed by C. glabrata (24%), C. parapsilosis (13%), and C. tropicalis (12%). Only 1.2% of C. albicans isolates were resistant to fluconazole (MIC, > or = 64 microg/ml), compared to 7% of C. glabrata isolates and 6% of C. tropicalis isolates. Only 0.9% of C. albicans isolates were resistant to itraconazole (MIC, > or = 1 micro g/ml), compared to 19.5% of C. glabrata isolates and 6% of C. tropicalis isolates. Only 4.3% of C. albicans isolates were resistant to flucytosine (MIC, > or = 32 microg/ml), compared to < 1% of C. parapsilosis and C. tropicalis isolates and no C. glabrata isolates. As determined by E-test, the MICs of amphotericin B were > or = 0.38 microg/ml for 10% of Candida isolates, > or =1 microg/ml for 1.7% of isolates, and > or = 2 microg/ml for 0.4% of isolates. Our findings highlight changes in the epidemiology of Candida BSI in the 1990s and provide a basis upon which to conduct further studies of selected high-risk subpopulations.
Figures
References
-
- Abi-Said, D., E. Anaissie, O. Uzun, I. Raad, H. Pinzcowski, and S. Vartivarian. 1997. The epidemiology of hematogenous candidiasis caused by different Candida species. Clin. Infect. Dis. 24:1122-1128. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, S. N., T. G. Emori, D. H. Culver, R. P. Gaynes, W. R. Jarvis, T. Horan, J. R. Edwards, J. Tolson, T. Henderson, and W. J. Martone. 1991. Secular trends in nosocomial primary bloodstream infections in the United States. Am. J. Med. 91:86-89. - PubMed
-
- Bodey, G. P., M. Mardani, H. A. Hanna, M. Boktour, J. Abbas, E. Girgawy, R. Y. Hachem, D. P. Kontoyannis, and I. Raad. 2002. The epidemiology of Candida glabrata and Candida albicans fungemia in immunocompromised patients with cancer. Am. J. Med. 112:380-385. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2000. Monitoring hospital-acquired infections to promote patient safety—United States, 1990-1999. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 49:149-153. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials