BMP10 is essential for maintaining cardiac growth during murine cardiogenesis
- PMID: 15073151
- PMCID: PMC2628765
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.01094
BMP10 is essential for maintaining cardiac growth during murine cardiogenesis
Abstract
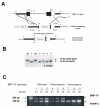
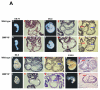
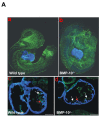
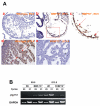
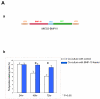
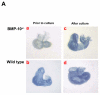
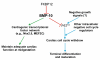
During cardiogenesis, perturbation of a key transition at mid-gestation from cardiac patterning to cardiac growth and chamber maturation often leads to diverse types of congenital heart disease, such as ventricular septal defect (VSD), myocardium noncompaction, and ventricular hypertrabeculation. This transition, which occurs at embryonic day (E) 9.0-9.5 in murine embryos and E24-28 in human embryos, is crucial for the developing heart to maintain normal cardiac growth and function in response to an increasing hemodynamic load. Although, ventricular trabeculation and compaction are key morphogenetic events associated with this transition, the molecular and cellular mechanisms are currently unclear. Initially, cardiac restricted cytokine bone morphogenetic protein 10 (BMP10) was identified as being upregulated in hypertrabeculated hearts from mutant embryos deficient in FK506 binding protein 12 (FKBP12). To determine the biological function of BMP10 during cardiac development, we generated BMP10-deficient mice. Here we describe an essential role of BMP10 in regulating cardiac growth and chamber maturation. BMP10 null mice display ectopic and elevated expression of p57(kip2) and a dramatic reduction in proliferative activity in cardiomyocytes at E9.0-E9.5. BMP10 is also required for maintaining normal expression levels of several key cardiogenic factors (e.g. NKX2.5 and MEF2C) in the developing myocardium at mid-gestation. Furthermore, BMP10-conditioned medium is able to rescue BMP10-deficient hearts in culture. Our data suggest an important pathway that involves a genetic interaction between BMP10, cell cycle regulatory proteins and several major cardiac transcription factors in orchestrating this transition in cardiogenesis at mid-gestation. This may provide an underlying mechanism for understanding the pathogenesis of both structural and functional congenital heart defects.
Figures







References
-
- Andree B, Duprez D, Vorbusch B, Arnold HH, Brand T. BMP-2 induces ectopic expression of cardiac lineage markers and interferes with somite formation in chicken embryos. Mech Dev. 1998;70:119–131. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Shen X, Shen K, Liu Y, Wang XF. The mammalian Rad24 homologous to yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad24 and Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rad17 is involved in DNA damage checkpoint. Cell Growth Differ. 1998;9:961–967. - PubMed
-
- Barron M, Gao Min., Lough J. Requirement for BMP and FGF signaling during cardiogenic induction in non-precardiac mesoderm is specific, transient, and cooperative. Dev. Mech. 2000;218:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Black BL, Olson EN. Control of cardiac development by the MEF2 family of transcription factors. In: Harvey RP, Rosenthal N, editors. Heart Development. Academia press; 1999. pp. 131–142.
-
- Chen F, Kook H, Milewski Rita., Gitler AD, Lu MM, Nazarian R, Schnepp R, Jen K, Biben C, Runke G, Mackay JP, Novotny J, Schwatz RJ, Harvey RP, Mullins MC, Epstein JA. Hop is an unusual homeobox gene that modulates cardiac development. Cell. 2002;110:713–723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

